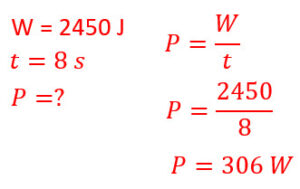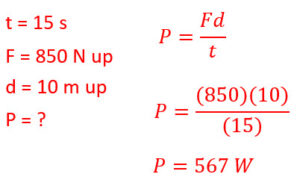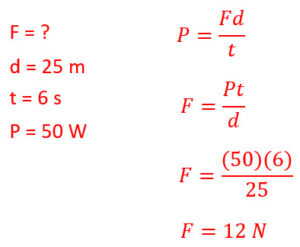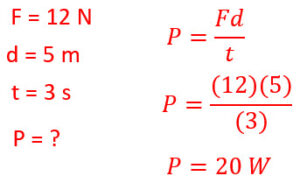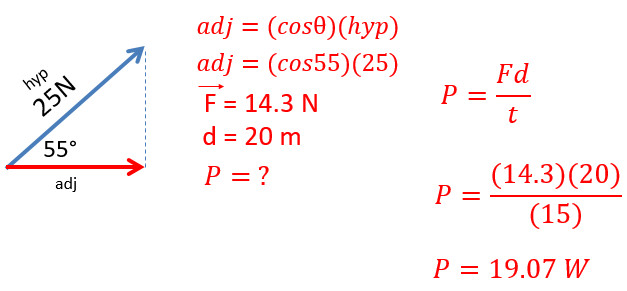Work and Power
Work is done any time you are transforming one form of energy into another. Power is the rate at which you do work. Learn more and see examples here.
Work
Work is done to transform energy from one form to another.
When lifting and dropping a rock:
- You do work to store Potential Energy (PE) as you apply a force to lift a rock a distance (height).
- Gravity does work converting potential energy (PE) to kinetic energy (KE) while the rock falls.
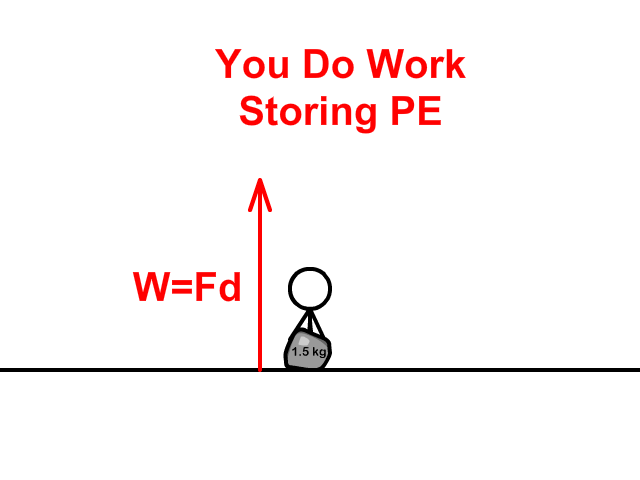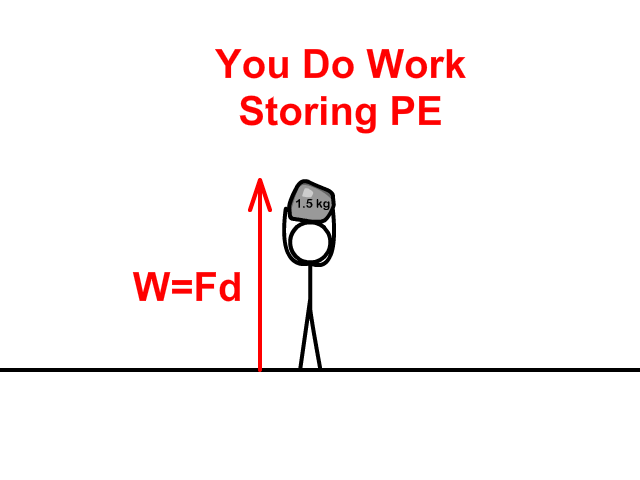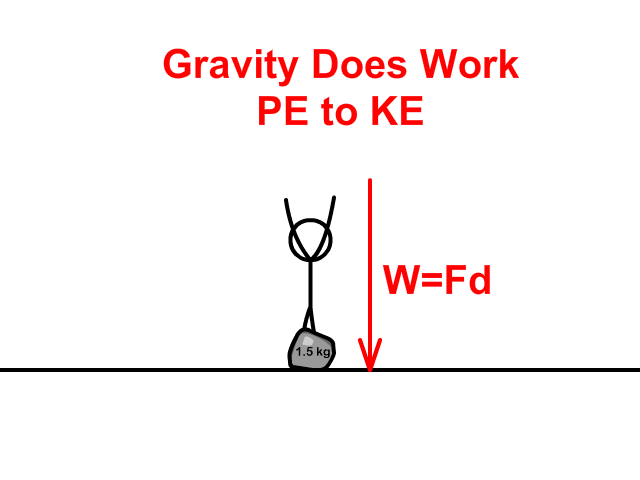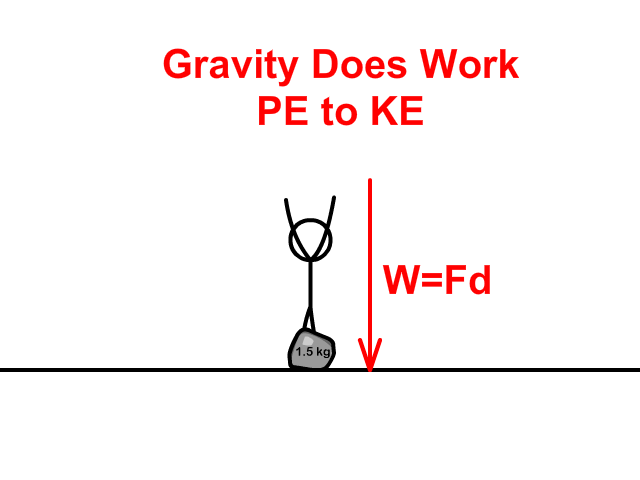
Joule (J) the MKS Unit of Work and Energy
- A joule (J) is equal to the work done by a force of one newton to move an object one meter in the direction of the force.
Work and Power Variables and Units
| Name | Variable | Unit | Unit Abbreviation |
| Work | W | Joules | J |
| Power | P | watt | W |
| Time | t | seconds | s |
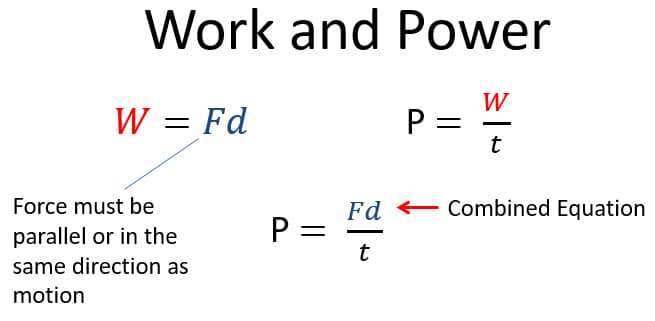
Work Equation Facts
- Work is force applied over a distance
- Work is only done if an object moves
- When applying force to an object that does not move, there is no work done. No matter how hard you push a wall, if it does not move, you do no work.

- Work is only done by the component of force in the same direction of motion
- If motion is up at a constant rate, the force is equal to the magnitude of weight of an object lifted
- (Fw = mg) and g is the acceleration due to gravity (g = 10 m/s2).
Click here to revisit the weight and mass page if you don' remember mass and weight)
Q1: How much work is done when a force of 50 N is applied to move a box 6 meters?
Q2: A student lifts a physics book applying a force equal to is 10 N weight a distance of 3 m up. How much work did the student do on the book?
Q3: How much work is done when a force of 50 N is applied but does not move a box?
Q4: Sergio pushed a box with 50 N of force forward. When it did not move he pushed the box even harder with 100 N of force but the box still did not move. When did Sergio do more work?
A) When he applied 50N of force
B) When he applied 100N of force
C) Neither
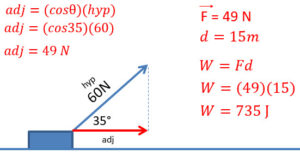
Work and Power When Force is at an Angle
- When force is at an angle, only the component in the direction of motion is used to calculate work or power (Here its seen in red)
- We are trying to determine the adjacent side in the picture
- This leads to cosine when we have the angle and hypotenuse
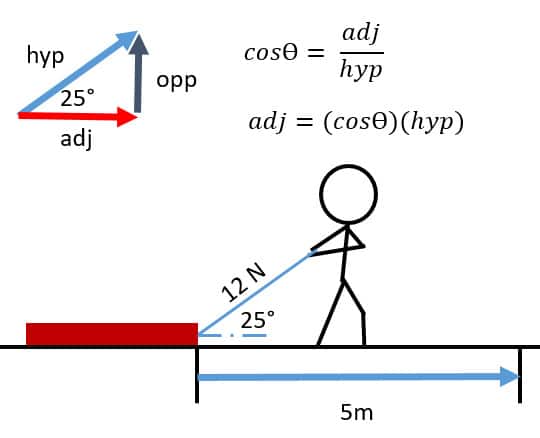
Q5: A sled is pulled by a boy with a force of 60 N at 35° from the horizontal. How much work is done if the sled moved 15 m forward?
Power
- Power is the rate at which work is done
- The unit of power is the watt (W)
- A watt equals a joule per second
Power is calculated as work divided by time. If you have force, distance, and time you can use the substituted formula you see here.
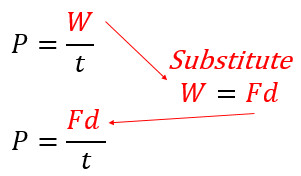
Q6: A car does 2450-J of work in 8 seconds. What is the power of the car?
Q7: Joe can go up a flight of stairs in 15 seconds. If the physics teacher weighs 850 N and the vertical height of the stairs is 10 m, what is Joe’s power output?
Q8: How much force is required to move an object 25 meters in 6 seconds with a power output of 50 watts?
Example Work and Power Problems
1. How much work is done to push a box 5 m with a force of 12 N forward?
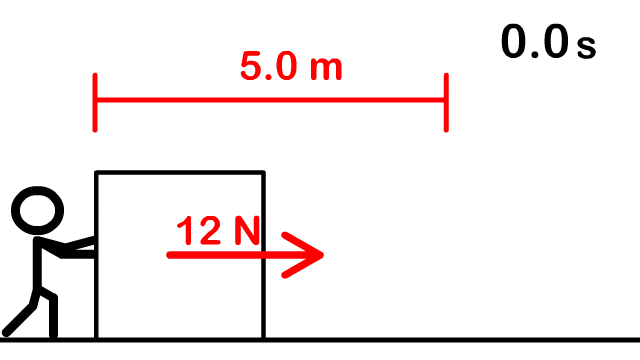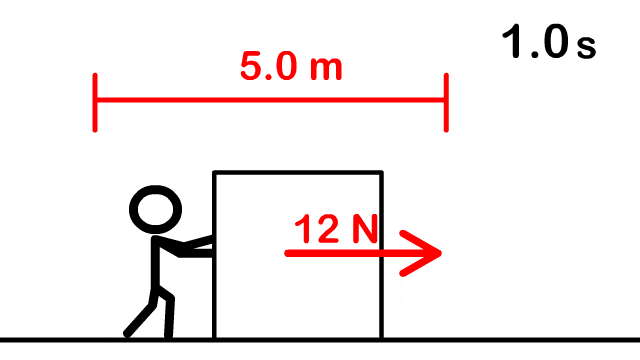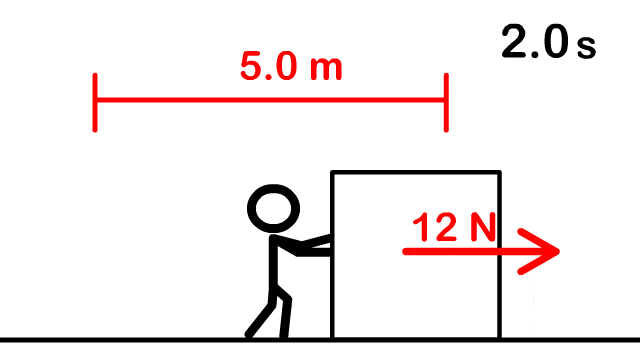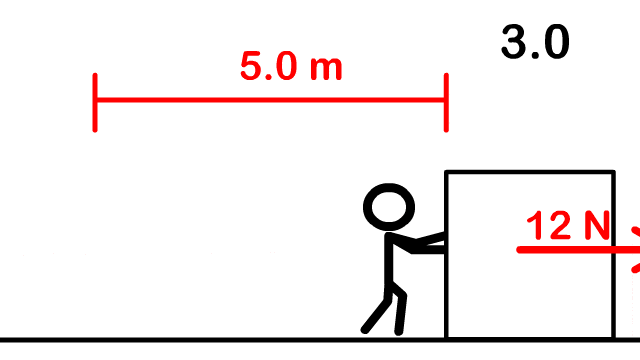
2. How much work is required to lift a 4 kg box at a constant rate a height of 2 meters?
3. What is the power output of a person that pushes the box 5 meters in 3 seconds with a constant force of 12 N?
4. How much work do you have when 12 N of force were applied on an object at an angle of 25° above the horizon to move an object 5 meters horizontally?
5. What is your power output when applying 12 N of force on an object at an angle of 25° above the horizon to move it 5 meters horizontally in 3 seconds?
6. A woman is pulling her luggage with a 25 N force at an angle of 55°. What is her power output if it takes her 15 seconds to pull the suitcase 20 forward?
Work and Power Practice Quiz
Links
- Continue to the Next Section: Mechanical Energy
- Back to the Main Work, Power, Mechanical Energy, and Simple Machines Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet