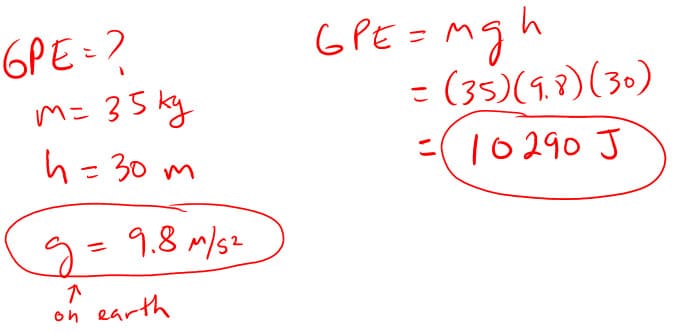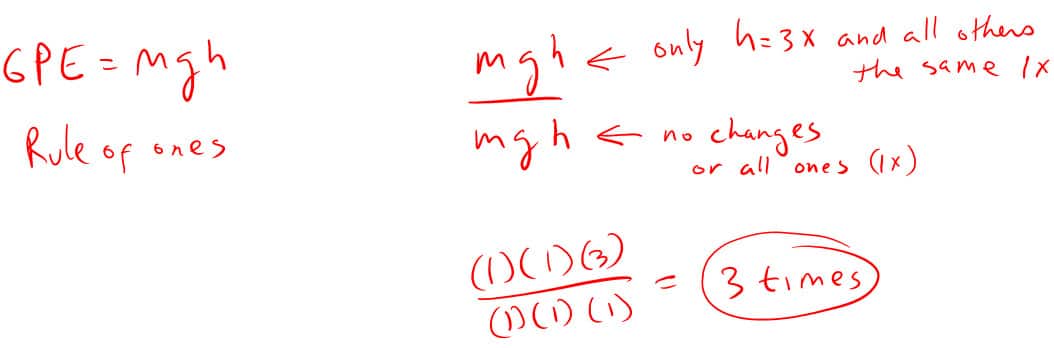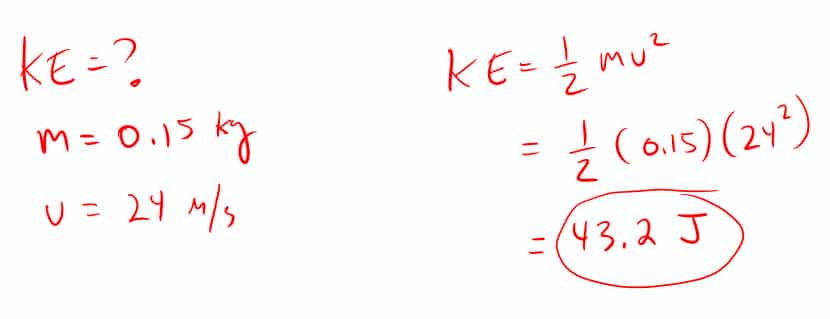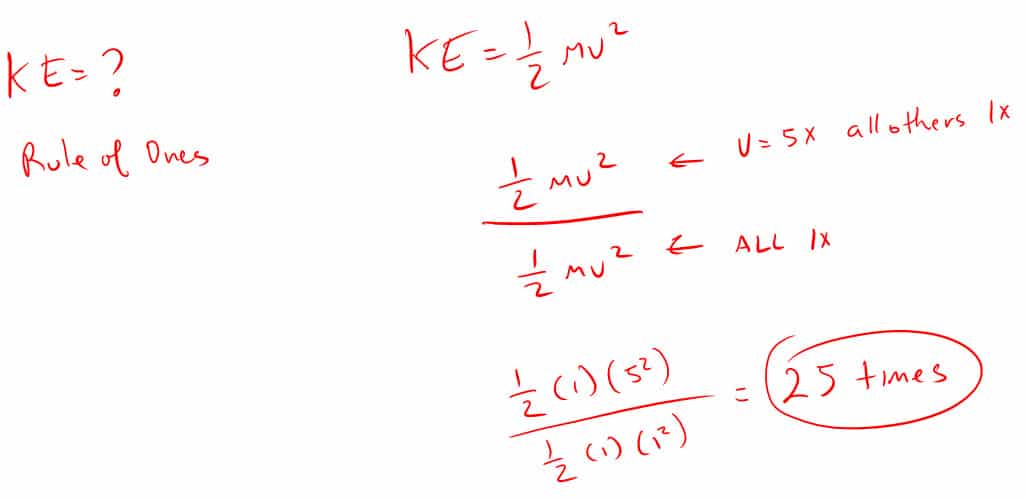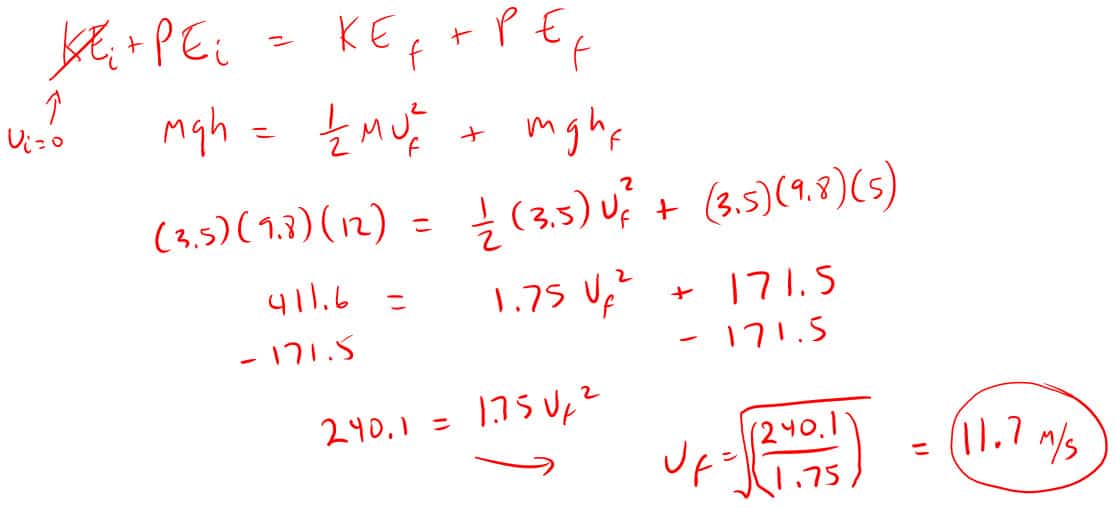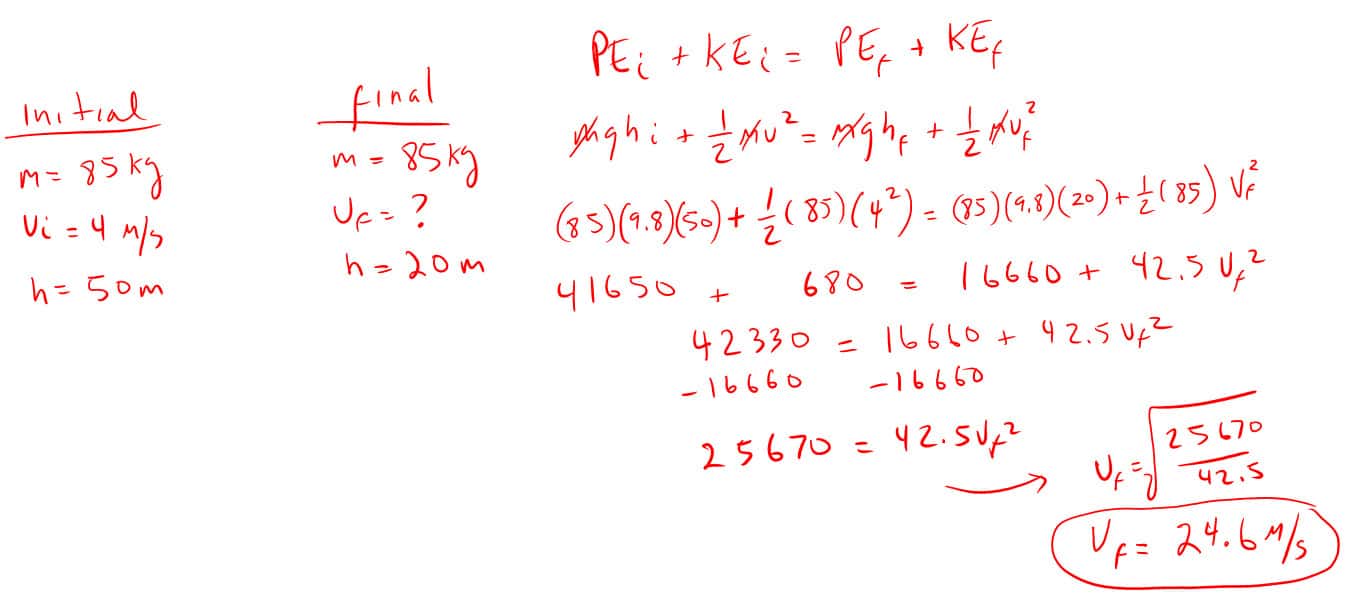Mechanical Energy Problems and Solutions
See examples of mechanical energy problems involving kinetic energy, potential energy, and the conservation of energy. Check your work with ours.
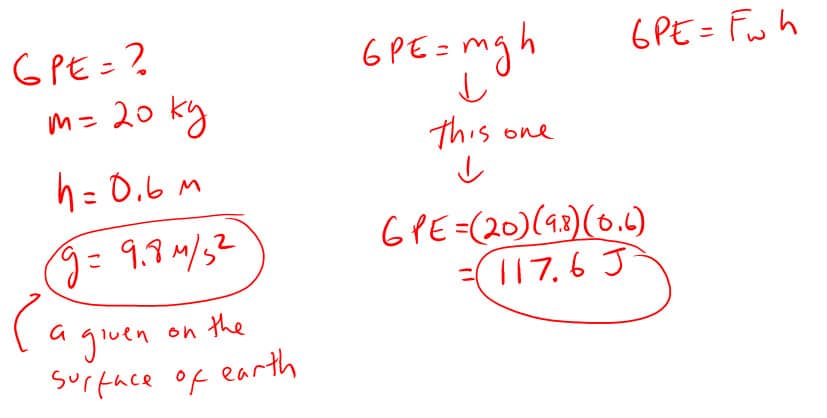
1. How much gravitational potential energy do you have when you lift a 15 N object 10 meters off the ground?
4. How many times greater is an objects potential energy when three times higher?
If you need help on ratio problems click the link below:
Rule of Ones: analyzing equations to determine how other variables change
7. How much kinetic energy does a 1.2 kg ball have the moment it hits the ground 3.5 meters below when it starts from rest?
I cancelled out the initial kinetic energy because:
- KEi = ½ mvf2
- KEi = (½)(3.5)(02) = 0 J
I cancelled out the final potential energy because:
- PEf = mghf
- PEf = (3.5)(9.8)(0) = 0 J
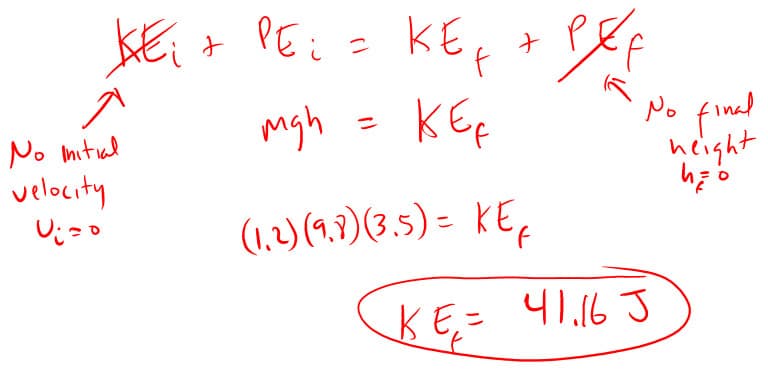
8. How fast is a 1.2 kg ball traveling the moment it hits the ground 3.5 meters below when it starts from rest?
I cancelled out the initial kinetic energy because:
- KEi = ½ mvf2
- KEi = (½)(3.5)(02) = 0 J
I cancelled out the final potential energy because:
- PEf = mghf
- PEf = (3.5)(9.8)(0) = 0 J
(Note: In many of these problems I could cancel out mass but did not since it was provided)
Since I did not cancel out mass I could answer the following questions if asked:
- How much mechanical energy did you have at the beginning? (41.6 J)
- How much kinetic energy did you have at the beginning? (0 J)
- How much potential energy did you have at the beginning? (41.6 J)
- How much potential energy do you have at the end? (0 J)
If I cancelled out mass in my work it would not show the actual initial potential energy since PEi = mgh and not just gh.
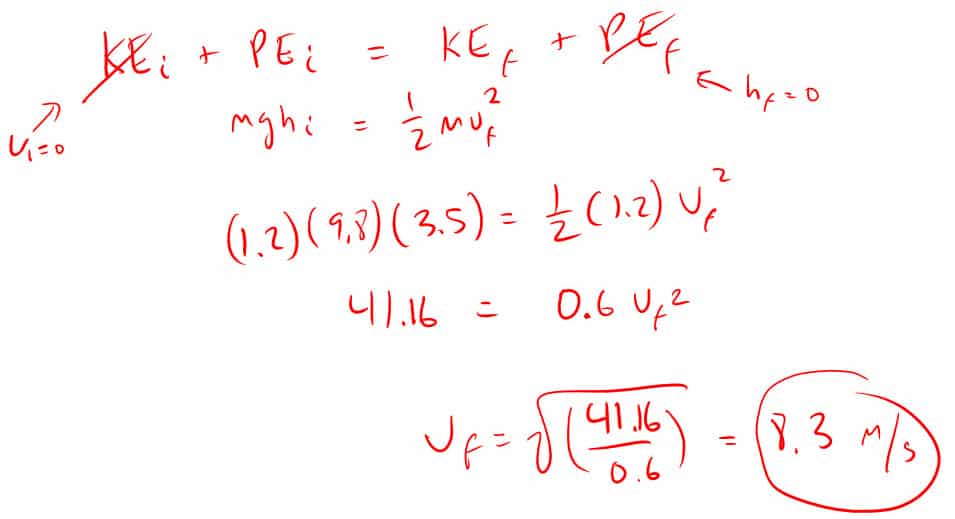
9. A 3.5 kg ball fell from a height of 12 meters. How fast is it traveling when its still 5 meters off the ground?
I cancelled out the initial kinetic energy because:
- KEi = ½ mvf2
- KEi = (½)(3.5)(02) = 0 J
10. An 85kg roller coaster cart is traveling 4 m/s at the top of a hill 50 meters off the ground. How fast is it traveling at top of a second hill 20 meters off the ground?
Links
- Back to the Mechanical Energy Page
- Back to the Main Work, Power, Mechanical Energy, and Simple Machines Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- For video tutorials and other physics resources check out HoldensClass.com
- Find many of your animation resources in one place at the StickMan Physics Gallery
- Equation Sheet