Electrostatics Review
Review some basic electrostatics content and equations with our practice problems that review the basics of our electrostatics unit.
You can click on see answer to quickly check an answer or see a more detailed explanation and the the work to any problem by watching the video here.
Electrostatics Practice Problems
Would you have and attraction or repulsion with the following charge +6 C and +5 C
Would you have and attraction or repulsion with the following charge +6 C and -5 C
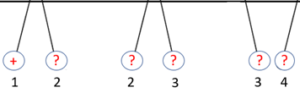
What would be the charges on each of the unknown spheres? (draw the charge symbol next to the numbers below)
Would the following increase or decrease electrostatic force between two charged objects
________Doubling the charge on an object
________Doubling the distance between objects
________Halving the charge on one object
________Doubling the charge on one object and doubling the distance between the objects
How much would the electrostatic force change if you doubled one charge and tripled the distance between objects?
How would you describe the relationship between force and charge using Coulombs Law?
How would you describe the relationship between force and distance using Coulombs Law?
What is an electrical conductor?
What is an electrical insulator?
Describe what causes and is occurring when someone gets shocked
Describe what causes you hair to stand up when charged
An object becomes negatively charged when ___________ move __________ the object.
An object becomes positively charge when ____________ move ___________ the object.
Describe charging by friction
Provide two examples of material rubbed together and the charges that would result on each using the electron affinity table.
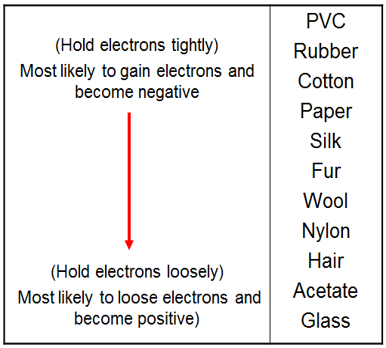
Describe charging by induction
Describe charging by conduction
What must be done to store electrical potential energy?
Describe electrical potential and how it is different than electrical potential energy?
A 7.5x10-7 C charge is placed 2. 0x10-2 m away from a 2.1x10-6 C charge. Find the electrostatic force that these two charges exert on each other.
How far away is a charge of 1.4x101 C from a 4.0x101 C charge when there is a force of 5.1x108 N between them?
What is the magnitude of the electric field that produces a force of 1.1x10-7 N on a charge of 5.0x10-10 C?
How much potential energy is requires to send 2.19x104 C of charge to create a voltage of 1.7x101 V?
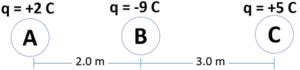
How much force would be on charge A in the diagram below and in what direction?
Links
- Back to the Electrostatics Main Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet