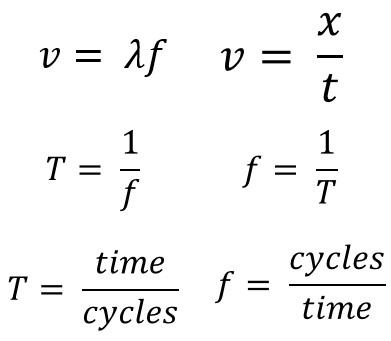Wave Math
Learning Targets
- Learn how to calculate the velocity of a wave and pick the right equation.
- Use the v = x/t and v = (𝜆)(f) to solve for different variables.
- Understand how wavelength and frequency are inversely related
- Solve for frequency an period using (T=1/f) or cycles and time.
Wave Equation Variables
In this section we will start by reviewing our basic equations when it comes to waves. Later we will add additional equations and forms of the ones you see here.
| Variable | MKS Unit | Unit Abbreviation | |
| Velocity | v | Meters per second | m/s |
| Wavelength | 𝜆 | meters | m |
| Frequency | f | Hertz | Hz |
| Displacement | x | meters | m |
| Time | t | seconds | s |
| Period | T | seconds | s |
Period is not just time but more specific. Period it the time that a simple harmonic motion event takes to happen. Simple harmonic motion is a continuous back and forth motion around an equilibrium position.
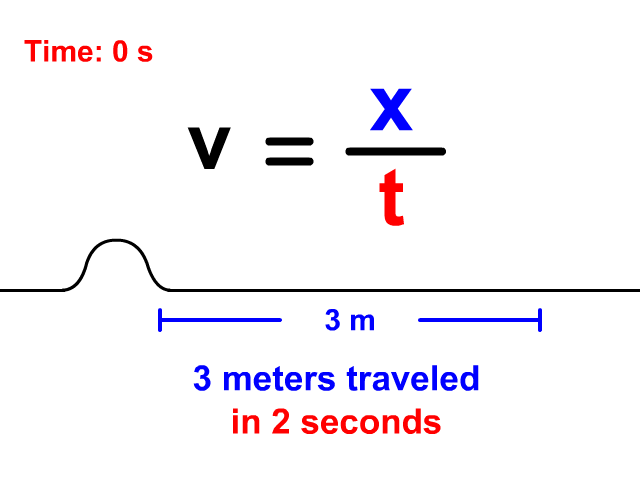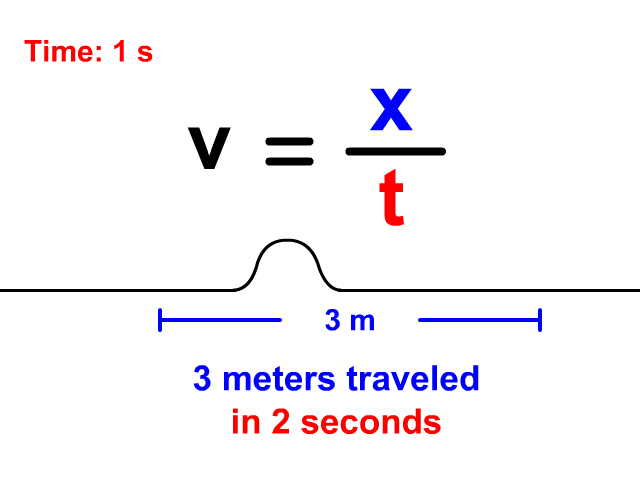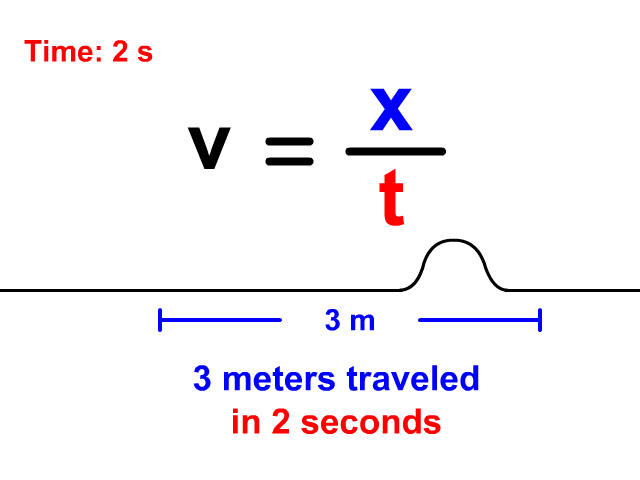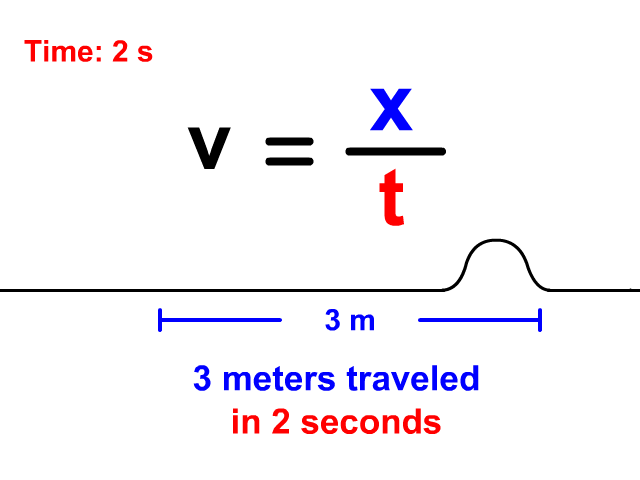
Velocity Equals Distance Divided By Time
When a wave is treated like an object traveling a displacement in a time, v = x/t is the equation you will use. Notice in the animation that the wave travels 3 meters in a total of 2 seconds. The resulting velocity using v = x/t is 1.5 meters per second.
v = x/t
v = 3/2 = 1.5 m/s
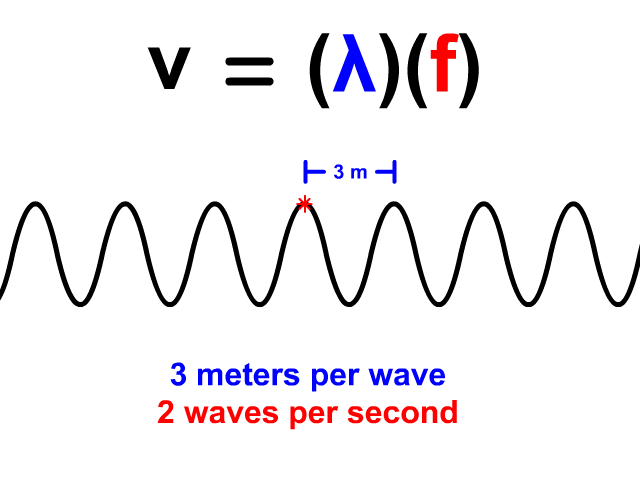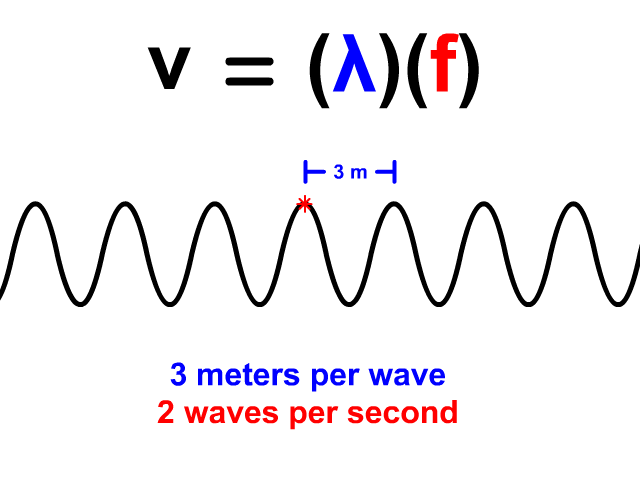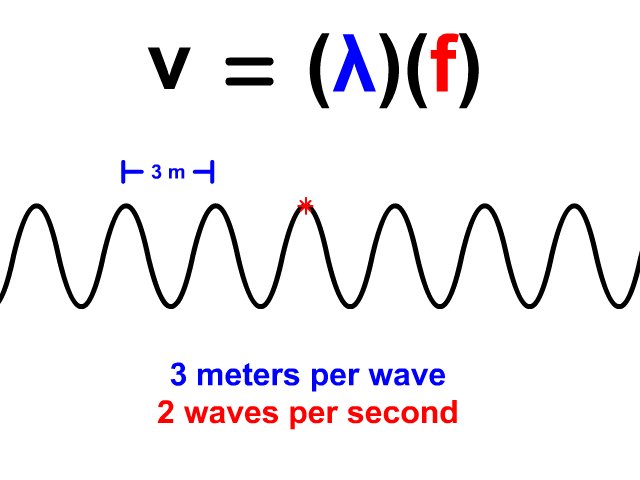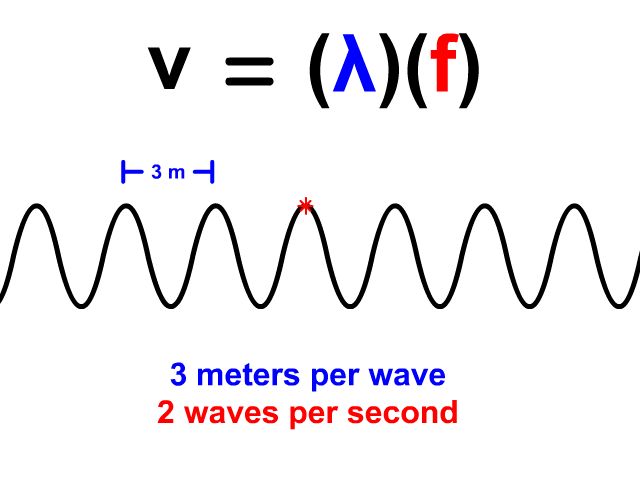
Wave Velocity Equals Wavelength Times Frequency
When you have a wave train, continuous waves each with the same wavelength (𝜆) pass a point. The frequency (f) of a wave is how many waves pass a point per second. When you have both wavelength and frequency you can use the equation v = 𝜆f to determine velocity. Frequency's standard unit is Hertz (Hz). Hertz equivalent unit is waves per second. 2 Hz means that two waves pass a point in a second. In our animation, each wave is three meters long. The frequency is 2 Hz so two waves pass each second. The resulting velocity using v = 𝜆f is 6 meters per second.
v = 𝜆f
v = (3)(2) = 6 m/s
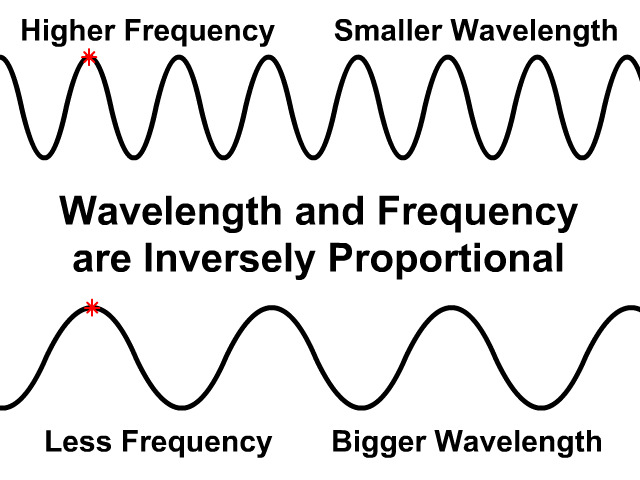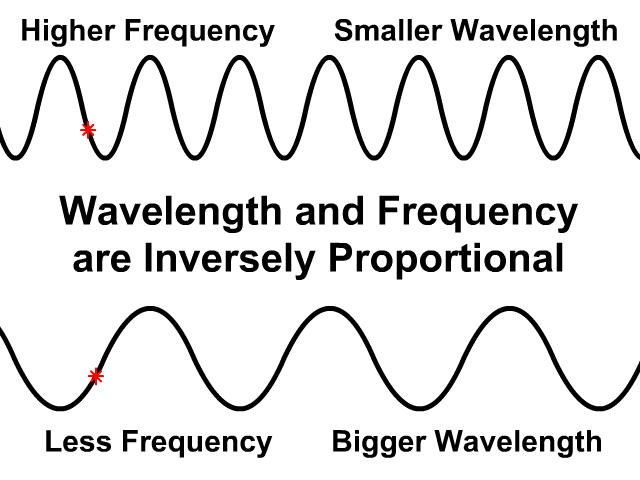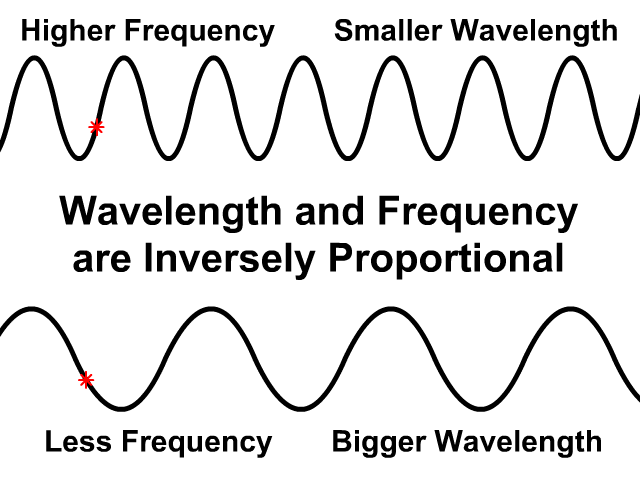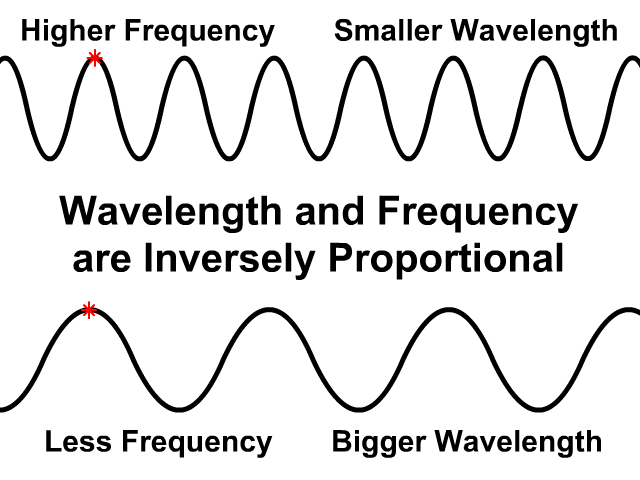
Wavelength and Frequency are Inversely Proportional
In the same medium wave speed will be the same
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional
- If wavelength is greater frequency will be less
- If frequency is greater wavelength will be less
Observe how the wave speed stays the same on the top and bottom animation. The bottom animation has a larger wavelength but lower frequency. Fewer waves pass by in the same amount of time.
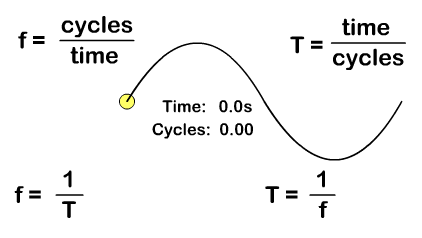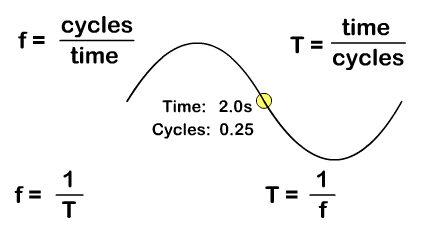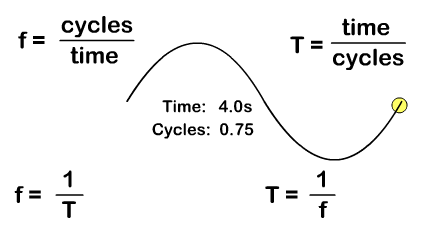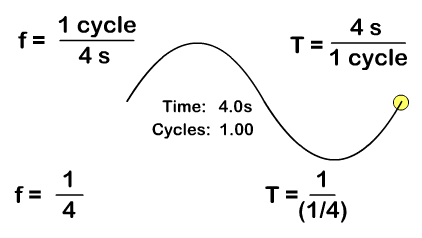
Wave Period and Frequency
A period (T), with a standard measurement in seconds, is not just time but time it takes to do something that is repetitive. A period for a wave is the time it takes for a complete wavelength. You can solve for period from the number of cycles "or waves" and time with the formula:
T = time/cycles
Frequency (f), with a standard measurement in Hertz, is how many repetitions occur per second. You can solve for frequency from the number of "wave" cycles and time with the formula:
f = cycles/time
Frequency and period are inverse since frequency is cycles per time and period is time per cycles. Solve for either with the either frequency or period as a given by taking the inverse:
T = 1/f f = 1/T
In the animation you see one "wave" cycle taking four seconds and the resulting ways you can solve for period or frequency.
Example Problems
1. A typical tsunami wave can travel as fast as a jet plane at 194.4 meters per second while in deep waters of the ocean. If the ocean were entirely deep water, how long would it take a wave to travel from uninhabited island X to uninhabited island B 1,205,000 meters away?
2. At the shoreline, a tsunami travels around 8.5 m/s. How long would it take a tsunami to travel 500 meters from the shoreline of island B to the middle of the island?
3. On a hot summer day, 15 wave crests pass a surfer floating on a board in 45 seconds.
a. What is the frequency of this wave?
3. On a hot summer day, 15 wave crests pass a surfer floating on a board in 45 seconds.
b. What is the period of this wave?
4. What is the wavelength of a 94.1 x 106 Hz radio wave traveling through air at 3.0 x108 m/s?
5. Velocity, average wavelength, and average frequency of the 7 types of electromagnetic waves in space.
| Radio | Microwave | Infrared | Visible | Ultraviolet | X-Ray | Gamma Ray | |
| Velocity in Air | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s | 3.0 x 108 m/s |
| Wavelength | 1 x 103 m | 1 x 10-2 m | 1 x 10-5 | 3.0 x 10-7 |
|
||
| Frequency |
|
1 x 1015 Hz | 1 x 1016 Hz | 1 x 1018 Hz | 1 x 1020 Hz |
Solve for the missing parts in the table
6. What is the velocity of a 900 Hz sound wave traveling through the air when the wavelength is 0.381 seconds per wave?
7. What is the period of a 900Hz sound wave?
A student records the following speeds for identical sound waves in three different mediums
(Use the table for #8, #9)
| Underwater | Air | Wood | |
| Speed of Sound (m/s) | 1,484 m/s | 343 m/s | 3,962 m/s |
8. What relationship could the student draw between the speed of sound and the type of medium based on this data?
A. As the medium gets denser, the speed of the sound wave increases
B. As the medium gets denser, the speed of the sound wave decreases
C. As the medium gets less dense, the speed of the sound wave increases
D. The density of the medium does not affect the speed of the sound wave
9. What is the frequency of a 1.855 m wave of sound traveling underwater at the speed in the table?
10. How many times different is frequency if wavelength has increased by three times?
Links
- On to Wave Phenomena
- Back to the Main Waves Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet