Newtons Third Law of Motion: Action Reaction Pairs
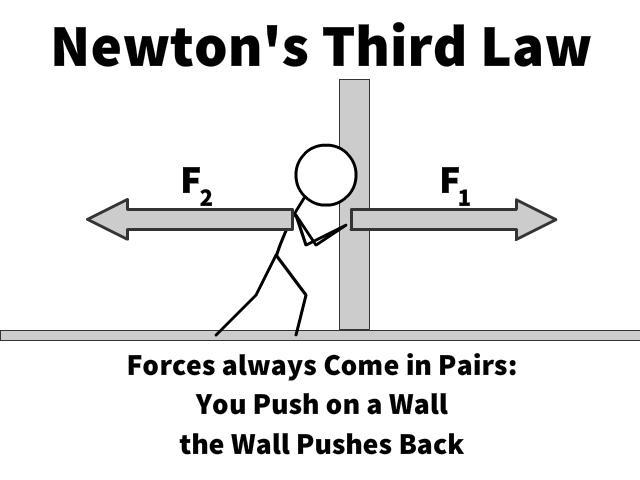
- The third law states that an applied force creates an equal and opposite force.
- When you push a wall the wall pushes you with equal force but in the opposite direction.
Learning Targets
- I know the main difference in Newton’s second and third law
- I understand what an action reaction pair is
- I can solve for the force, mass, or acceleration of two object that result from a force applied from one object to the other
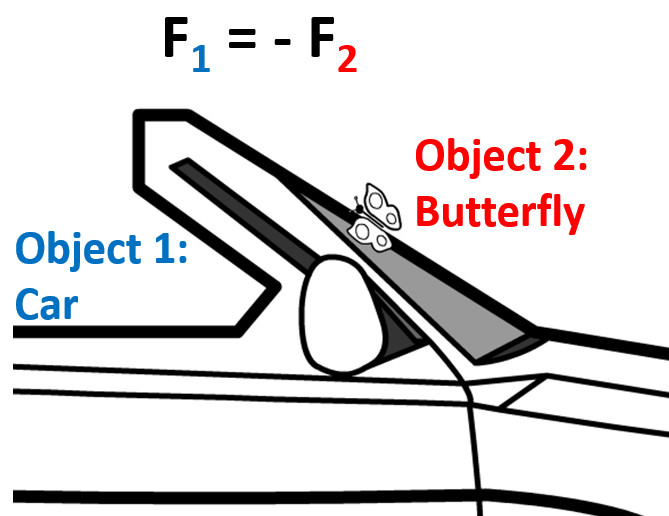
Q4: Does the car or butterfly exert more force when the butterfly hits and squishes against your windshield?
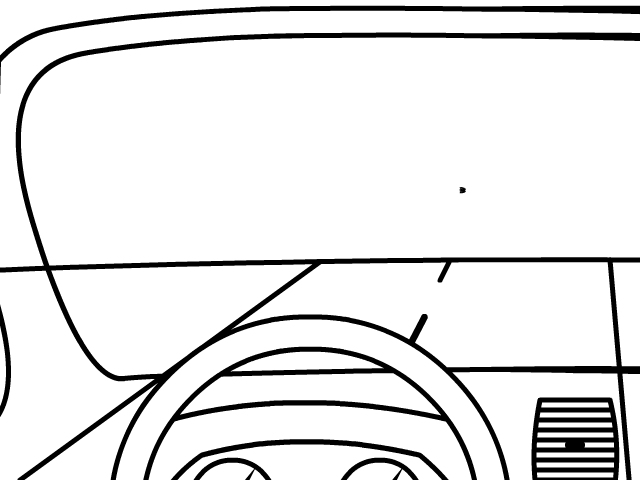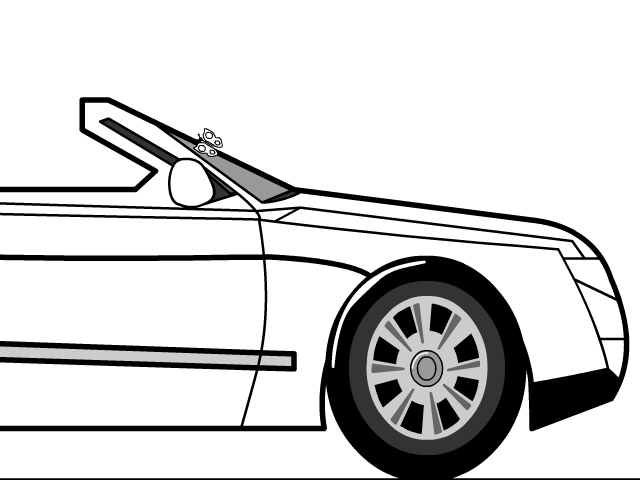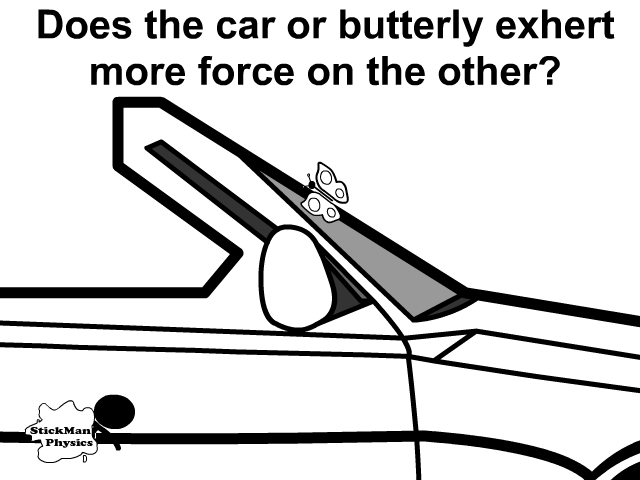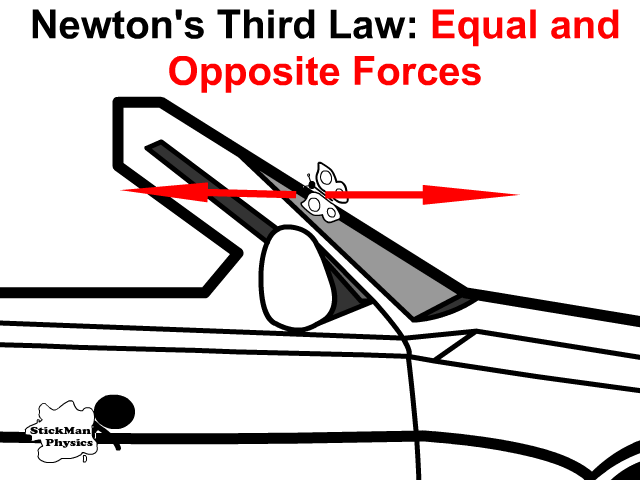
Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion (Action-Reaction Pairs)
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
This means that Forces always occur in pairs and are:
- equal in strength
- opposite in direction
Equation: F1 = -F2
- F1 = Force of the first object on second
- F2 = Force of the second object on first
Q5: What is the reaction force when a bat applies a 20 N force to a baseball?
Q6: What is the reaction force when the earth pulls a person down by his weight of 800 N?
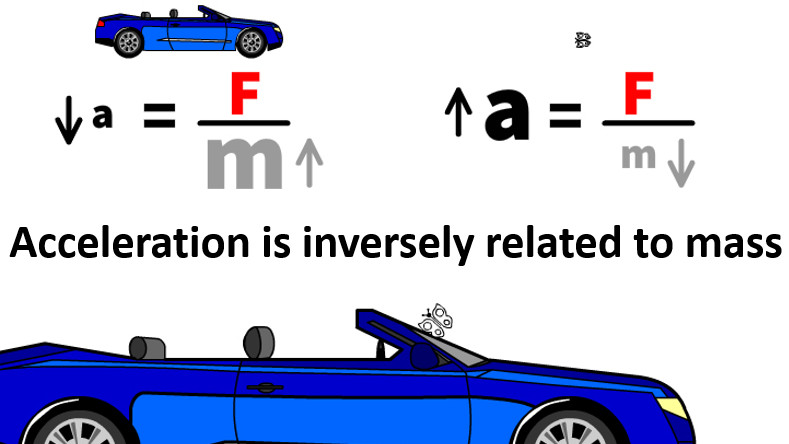
Same force but different mass results in different accelerations
- large mass means less acceleration
- small mass means more acceleration
Major differences between Newton’s 2nd and 3rd Law
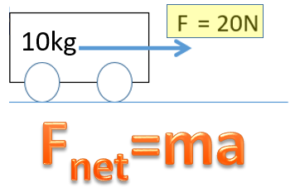
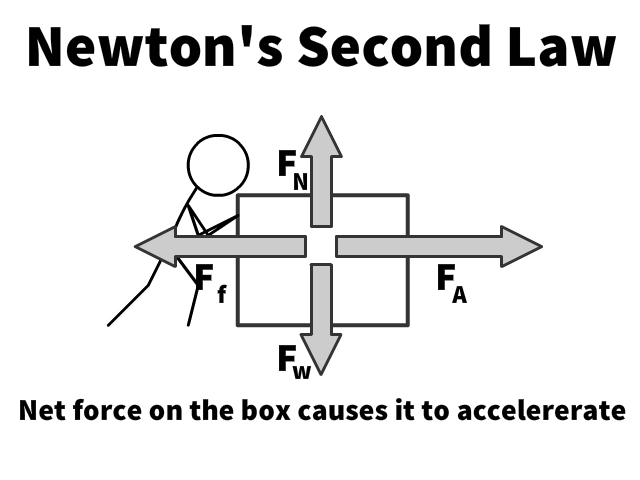
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion (Fnet = ma)
Involves one object and the net force resulting from all the forces creating that one object to accelerate
- Fnet = Sum of forces only on the box
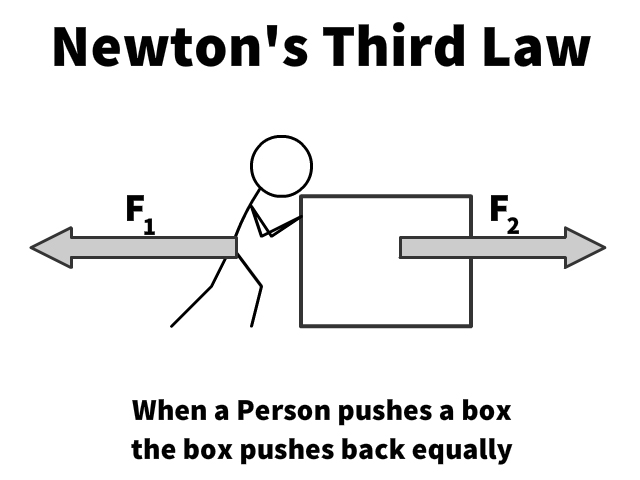
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion (Action-Reaction Pairs)
Involves two objects each with an equal and opposite force
-
- F1 = Force of the first object on second
- F2 = Force of the second object on first
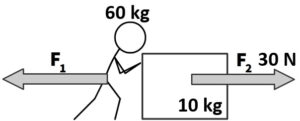
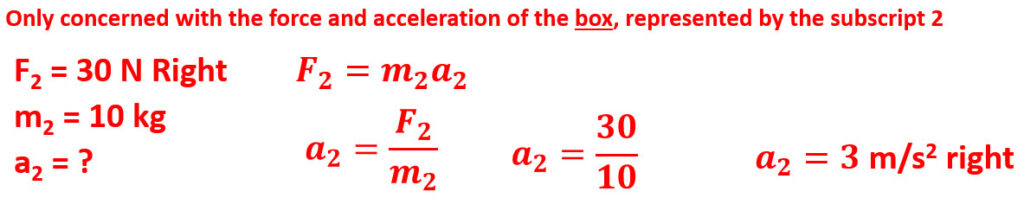
Q7: A 60 kg person pushes a 10 kg box with a force of 30 N to the right. What is the force on the person?
Q8: A 60 kg person pushes a 10 kg box with a force of 30 N to the right. What is the acceleration of the box?
Q9: A 60 kg person pushes a 10 kg box with a force of 30 N to the right. What is the acceleration of the person?
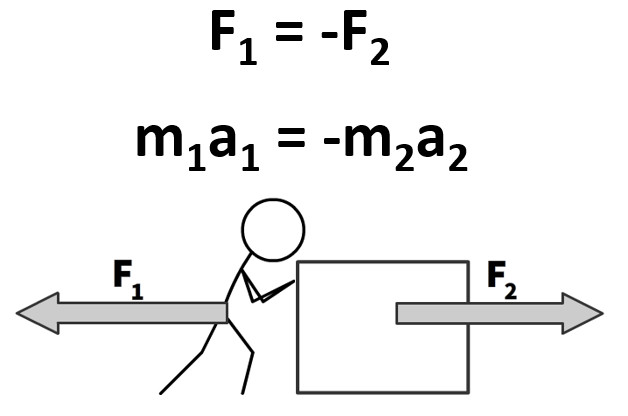
Newton's Third Law in equation form states
- F1 = -F2
Newton's Second Law states net force causes acceleration on an object
Object 1
- F1 = m1a1
Object 2
- F2 = m2a2
With Substitution of F1 and F2 in Newton's 3rd Law Equation
- m1a1 = -m2a2
- The negative represents an opposite force causing an opposite acceleration
Q10: A 60 kg person pushes a 10 kg box that accelerates 25 m/s² to the right. What is the acceleration of the person while force is applied?
Q11: 95 kg Joe jumps off a 0.8 kg skateboard and he accelerates at 1.5 m/s² right what is the acceleration of the skateboard?
Problem Set
1A. What is the weight of a 50 kg child, the force the Earth pulls a child down by? (use g = 10 m/s2)
1B. What would the 50 kg child pull the earth up by?
(Use for #2A-C) 82 kg Tommy applies a force of 200 N on a 1,000 kg car while pushing it forward on a frictionless surface
2A. How much does the car accelerate?
2B. How much force does the Tommy feel from the car?
2C. How much does Tommy accelerate?
3. A 76-kilogram person jumps off a 100 kg canoe accelerating the canoe at 5.0 m/s2 right. What is the acceleration of the person?
(Use for #4A-C) 67 kilogram Jody swats at 0.012 kg bug that landed on her applying 15N of force to squish it.
4A. As a result Jody feels how much force? (Choose one)
A) Less than 15 N of force
B) More than 15 N of force
C) Exactly 15 N of Force
4B. What is the acceleration of the bug while the force is applied?
4C. Would the magnitude of Jody’s acceleration be
A) More than the bug
B) Less than the bug
C) Exactly the same as the bug
5A. When you push on a wall with 50 N of force the wall pushes you back with 50 N of force?
5B. When you hit cars breaks, your body leans forward.
5C. Joe and Jill both push a 159 kg refrigerator with a force of 200 Newtons and the refrigerator accelerates at 2.52 m/s2 forward.
Links
- Continue to Air Resistance
- Back to the Main Forces Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet