Isaac Newton and the Laws of Motion
Learning Targets
- I can define inertia
- I can describe how inertia is directly related to mass
Who was Sir Isaac Newton?
Sir Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, as well as writer that is commonly identified as one of the most influential scientists of all time. Newton's shaped the way we understand motion along with the universe as a whole.
Watch the brief Biography video to learn more
Isaac Newton’s Three Laws of Motion
- First Law: An object will maintain its state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an outside force (law of inertia)
- Second Law: Net Force Causes Acceleration (Fnet = ma)
- Thirds Law: An action force on one object creates an equal and opposite reaction force on the other object that created it (Action Reaction Pairs)
Newton's First Law of Motion: Inertia
Newton's First Law of Motion is the law of inertia. Inertia is an objects tendency to maintain its state of motion. So if it is at rest, it will stay at rest and if in motion, it will stay in that constant state of motion. This occurs unless acted upon by an outside force or forces that are unbalanced creating a net force not equal to zero.
No net force can occur because there are no forces acting on an object or all the forces are balanced and in equilibrium. Fnet= 0 N and acceleration = 0 m/s2 when there is no net force.
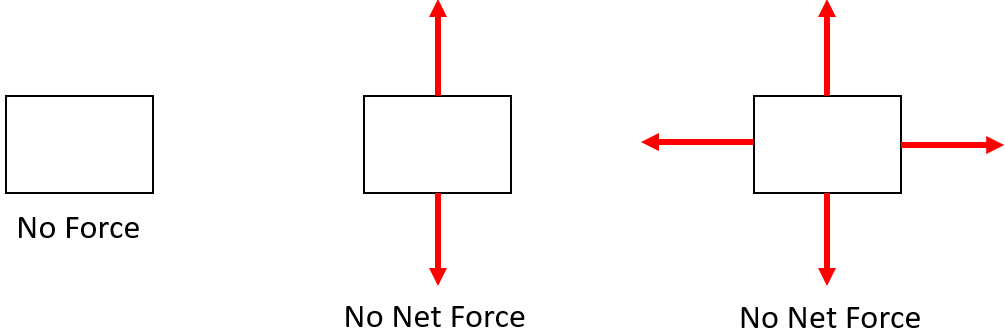
In all the situations seen in the three force diagrams, there is no net force and no acceleration. These objects could be at rest or moving with a constant velocity in a straight line.
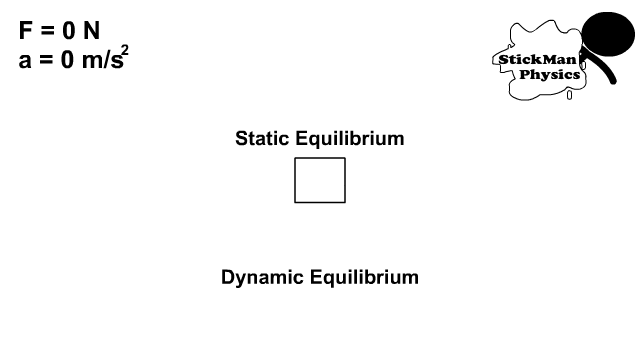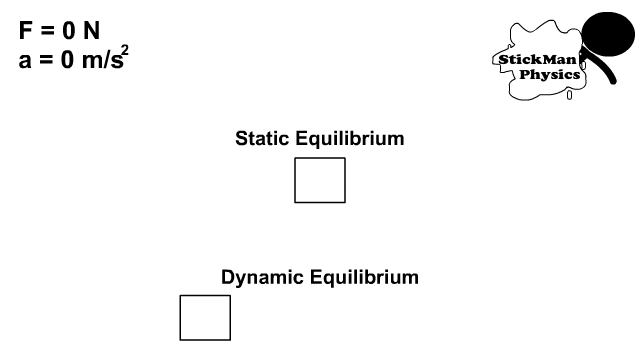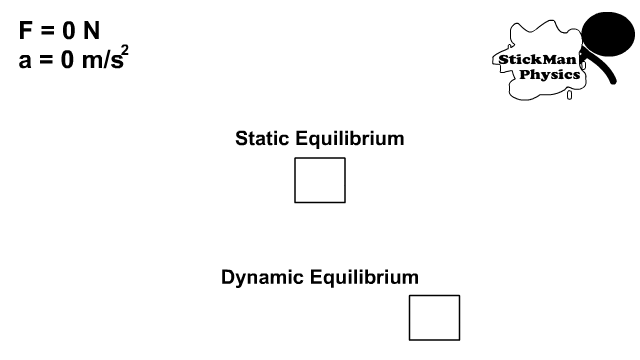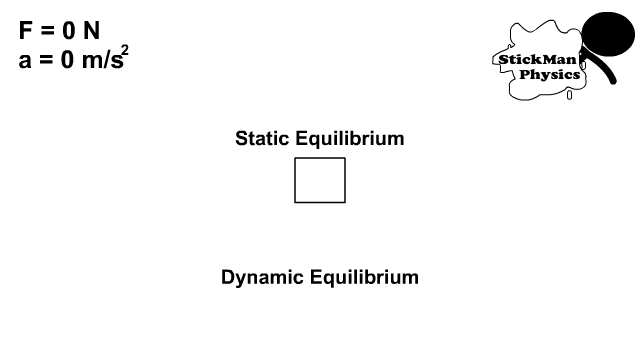
Static and Dynamic Equilibrium
- Static equilibrium is a state of being at rest with no net force
- Dynamic equilibrium is the state of being in constant motion with no net force
You, Your Car, and Inertia
Inertia makes your body want to keep going forward when in the car and you hit the brakes. Because of inertia, your body leans forward.
No force is required to get an object to move if it is already moving. A force is required to change an objects state of motion or rest.

Earth follows the laws of the universe
- On Earth, we have friction and air resistance ,which are opposing forces to motion. Object on Earth seem to stop naturally because gravity brings an object to the ground and friction stops them. Earth Still Has Inertia
- In the vacuum of space, you do not have air resistance. Objects like the moon, planets, and asteroids continue to move because they are already moving.
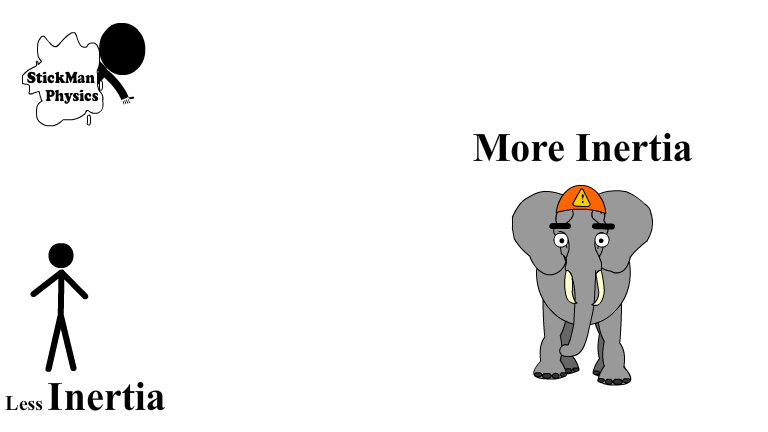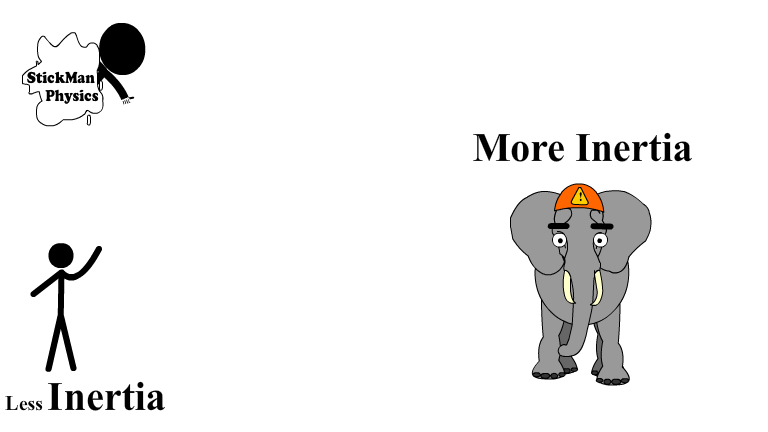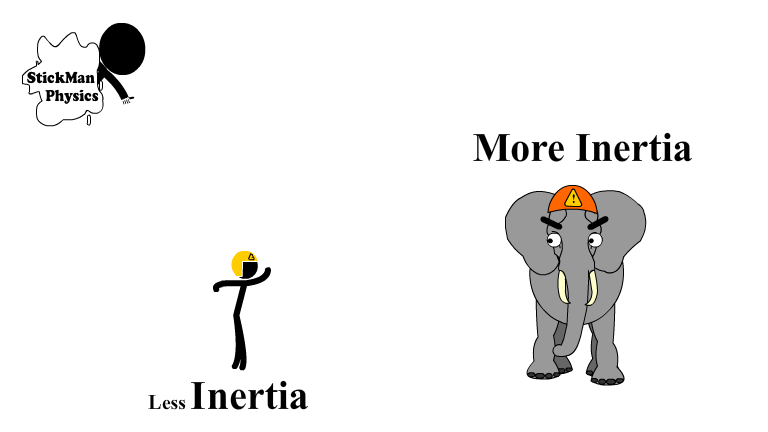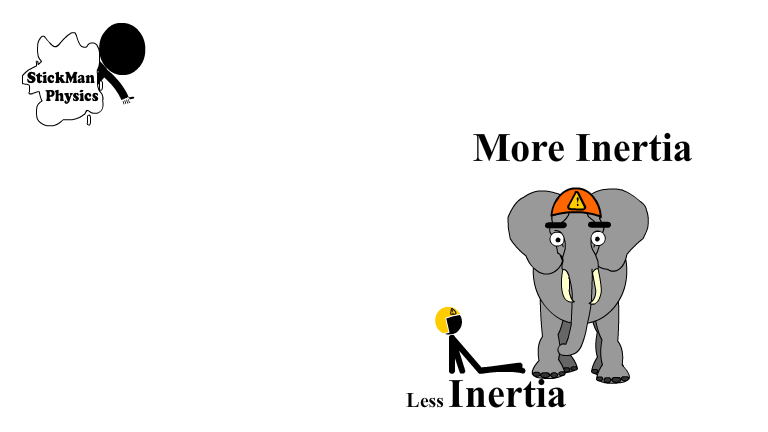
Inertia and Mass are Directly Related
Inertia is directly related to the mass of an objects. An 80 kg human has a whole lot less inertia than a 3000 kg elephant.
The elephant takes a lot more force to start or stop moving.
Q1: What is inertia?
Q2: How much force is required to get or keep an object moving? (Choose the best answer)
A) Anything above zero
B) Enough to overcome its inertia
C) None if it is already moving
Q3: Would a 0.5 kg toy car or a 1500 kg truck have more inertia and why?
Links
- Continue to Newtons Second Law of Motion
- Back to the Main Forces Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet
