Motors and Generators
Motors and generators are essential for modern technology and magnetic induction is the phenomenon that makes them work.
Electric Motors
An electric motor is a device that converts electric energy into mechanical energy (motion).
A basic electric motor will have an armature with current running through it and either another electromagnet or permanent magnet.
The standard armature is made up of a solenoid. The more solenoid coils and more current running through them, the stronger the electromagnet. The stronger the interacting magnetic fields the more powerful the motor.
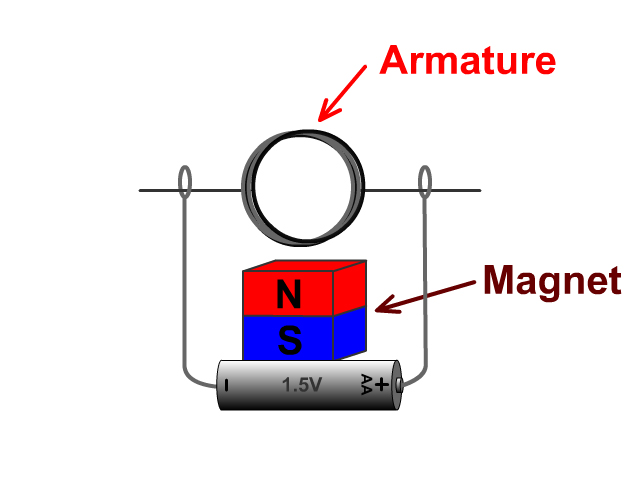
Current running through an armature causes the armature to become an electromagnet through magnetic induction. The armatures magnetic field interacts with another magnetic field creating motion.
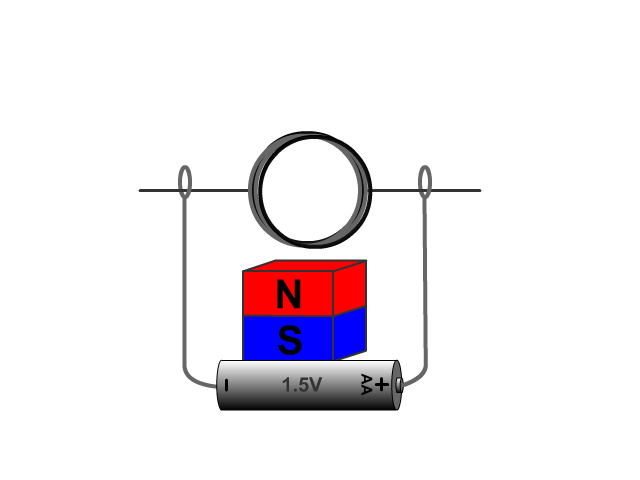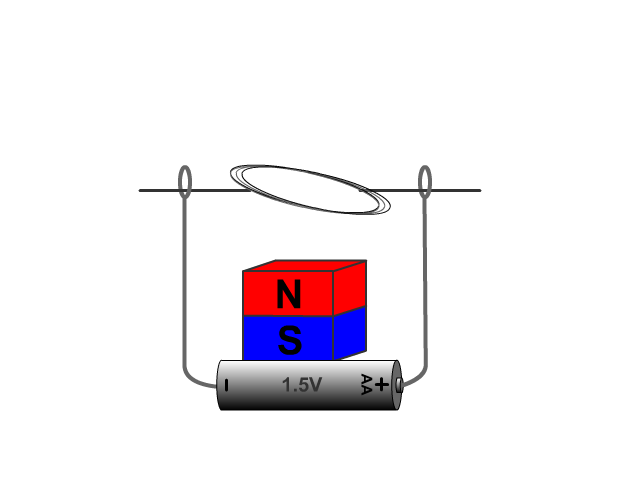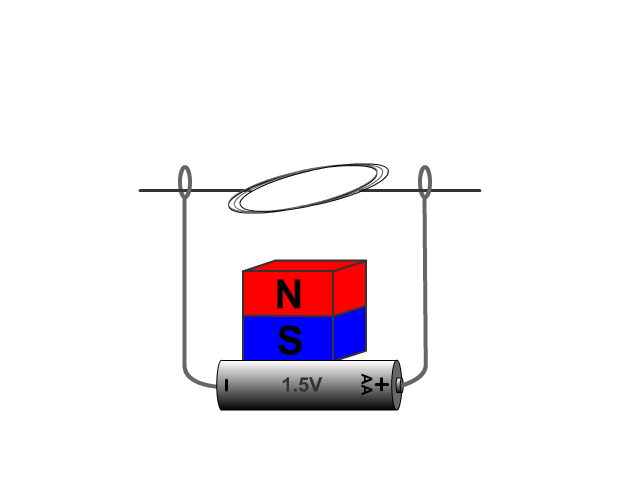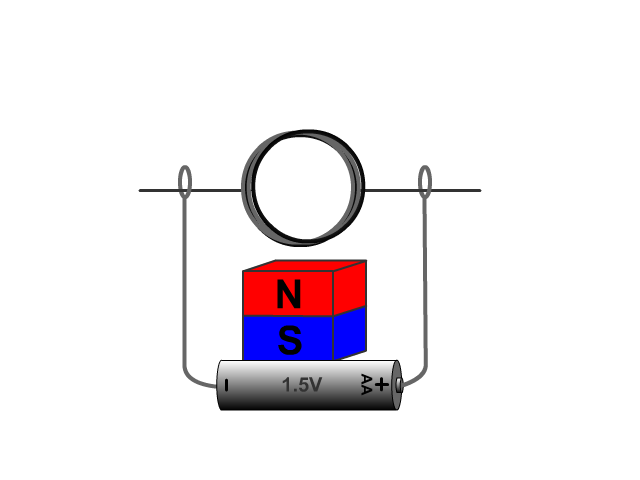
Electric Generators
An electric generator is the opposite of a motor. An electric generator converts mechanical energy (motion) into electric energy producing induced voltage and current.
For an electric generator an armature needs to rotate in a magnetic field produced by a magnet. The changing magnetic field as the armature rotates forces electrons through the armatures solenoid inducing current.
A basic hand generator can be seen in our animated model. No current is produced when the armature is not being rotated.
Today there are many types of power plants including fossil fuel, nuclear, solar, and hydroelectric used to rotate complex armatures and create electricity to be used or stored.
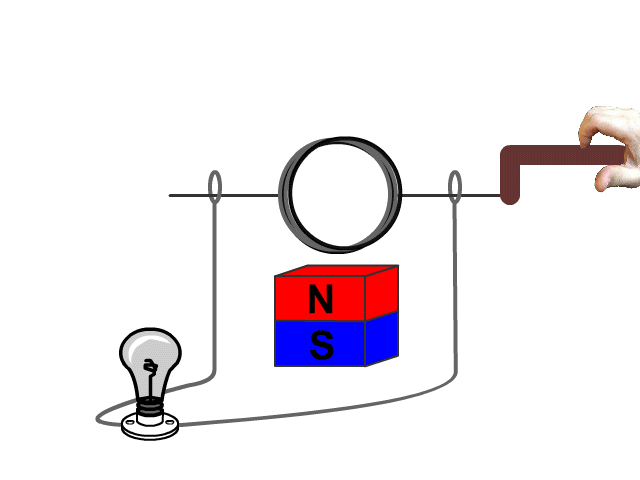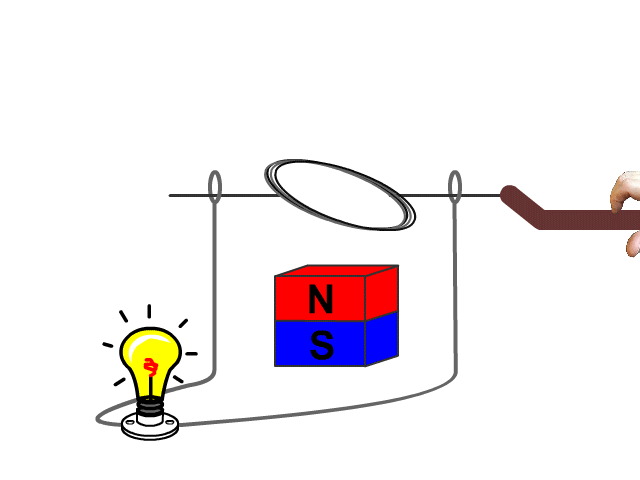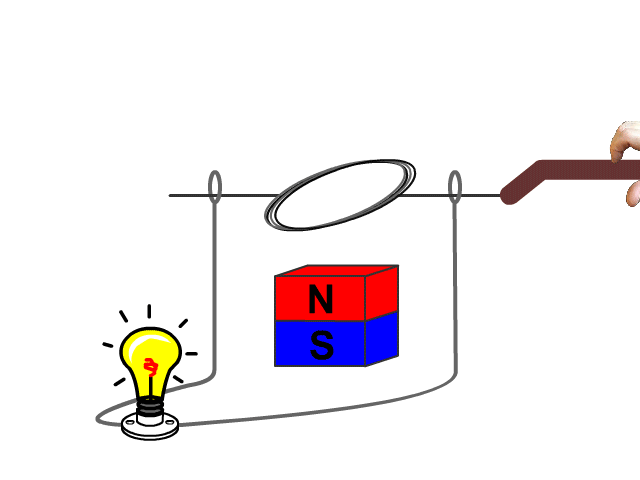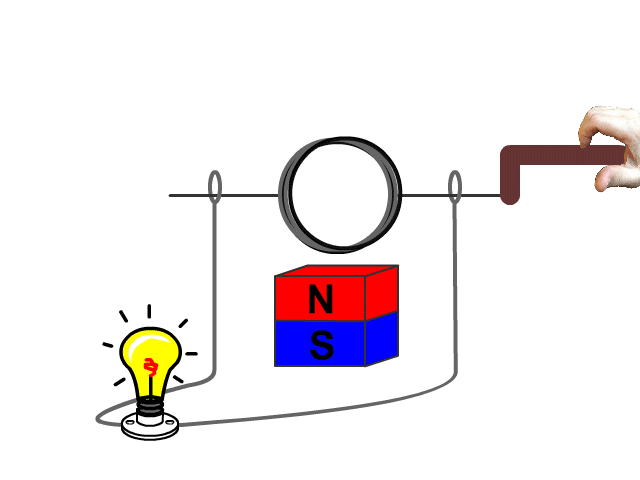
Example Problems
1. Which of the following devices consist of an armature and magnet interacting?
A. Electric Motor
B. Electric Generator
C. Both Electric Motor and Generator
2. Which of the following devices consist of an armature that must be rotated in a magnetic field to create current?
A. Electric Motor
B. Electric Generator
C. Both
3. What device can you use to turn electric energy into mechanical energy?
A. Electric Motor
B. Electric Generator
C. Both
4. An electric generator converts _________.
A. Mechanical energy into chemical energy
B. Mechanical energy into electric energy
C. Electric Energy into chemical energy
D. Electric energy into mechanical energy
5. An electric motor converts _________.
A. Mechanical energy into chemical energy
B. Mechanical energy into electric energy
C. Electric Energy into chemical energy
D. Electric energy into mechanical energy
6. The phenomenon of electrical generators that use changing magnetic fields to force current through a wire is ________________.
A. Magnetic Transduction
B. Magnetic Induction
C. Electric Induction
D. Electric Insulation
Links
- Back to the Main Magnets and Magnetism Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- For video tutorials and other physics resources check out HoldensClass.com
- Find many of your animation resources in one place at the StickMan Physics Gallery
- Equation Sheet
