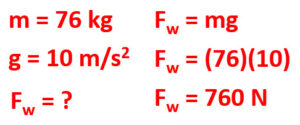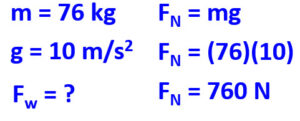Air Resistance
Learn about air resistance and terminal velocity. A frictional force caused by air particles while an object travels through the air.
Air Resistance Learning Targets
- I know how air resistance changes during a fall
- I know how to draw a free body diagram of a falling object
- I can determine net force and acceleration of an object
- I can describe terminal velocity
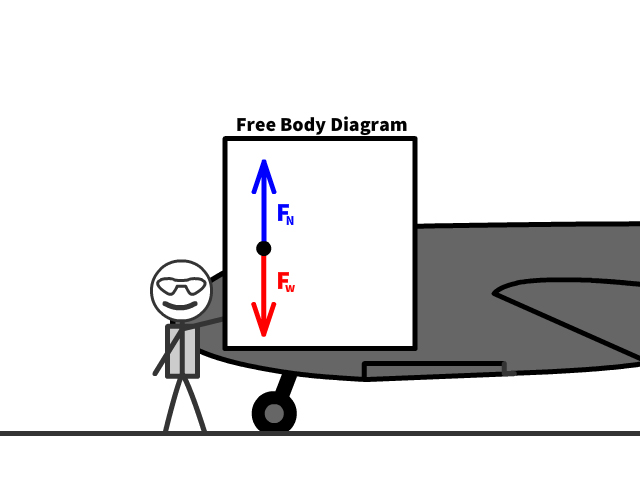
Free Body Diagrams
- A free body diagram shows all the vector forces and their direction acting on an object
- The dot in the middle represents the object
Air Resistance
- Air resistance is a force that pushes backwards as an object moves through the air
- The faster an object falls the greater the opposing air resistance
Air Resistance and a Vacuum
- A vacuum is an area without air molecules
- Space is also a vacuum. Vacuums can be created on earth by sucking out the air particles.
- Surface area affects the amount of air resistance under normal situations
- A greater surface area will collide with more air particles and increase air resistance

Q1: If Caleb has a mass of 76 kg, what is his weight on Earth with an acceleration due to gravity of 10 m/s²?
Normal force and weight on a horizontal surface
- Have the same magnitude
- Use the weight equation (Fw = mg) for magnitude of FN
- FN = mg but up
Q2: If Caleb has a mass of 76 kg, what is the normal force on him?
Q3: What is the net force on Caleb as he sits on a horizontal surfaced seat?
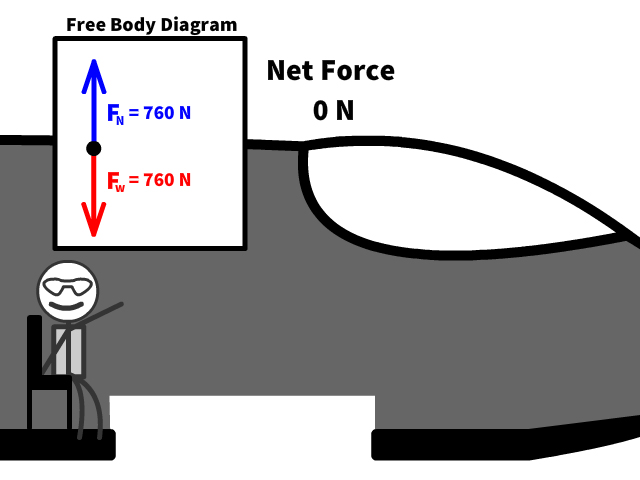
Q4: When 76 kg Caleb first jumps out, there is no air resistance. What is his acceleration at this point?
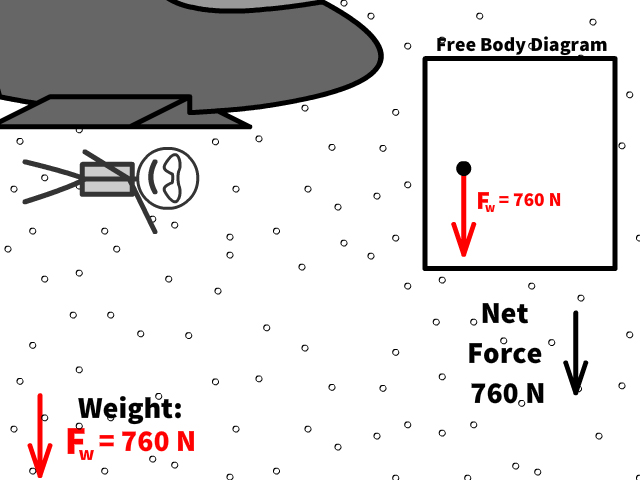
Q5: What is Caleb’s new net force when air resistance is 200 N?
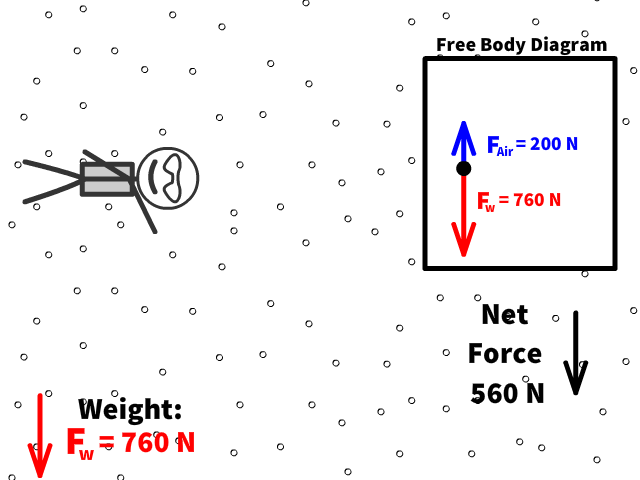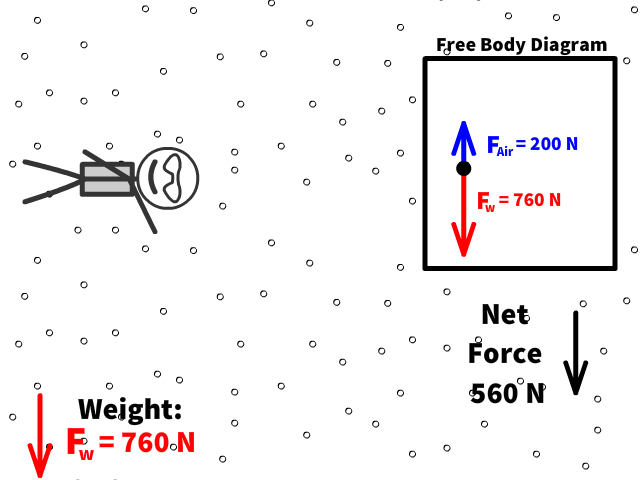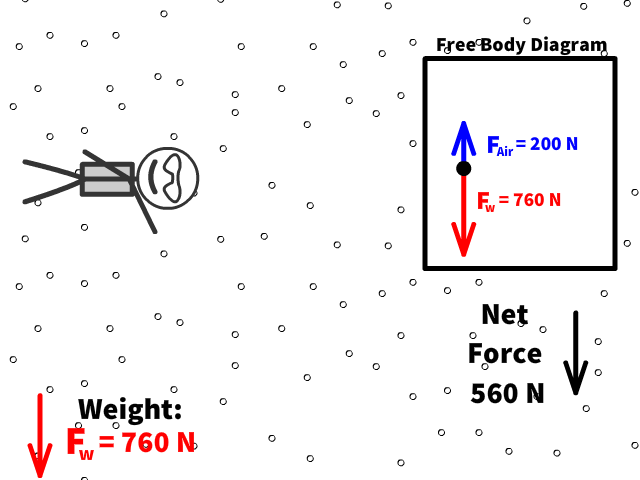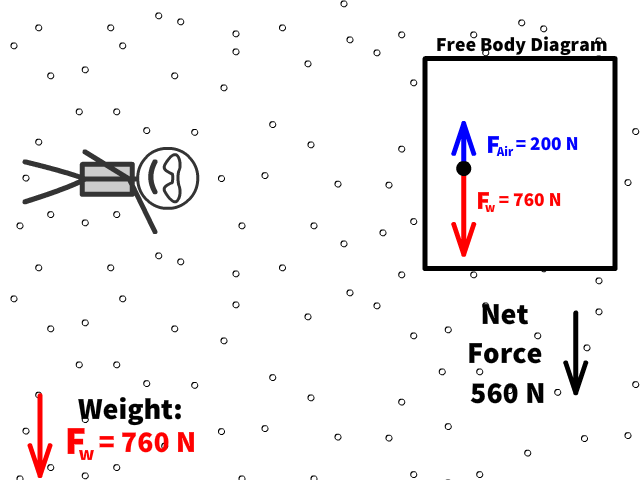
Q6: What is Caleb’s new acceleration with a net force when air resistance is 200 N up?
Q7: What is Caleb’s new net force when air resistance is 500 N?
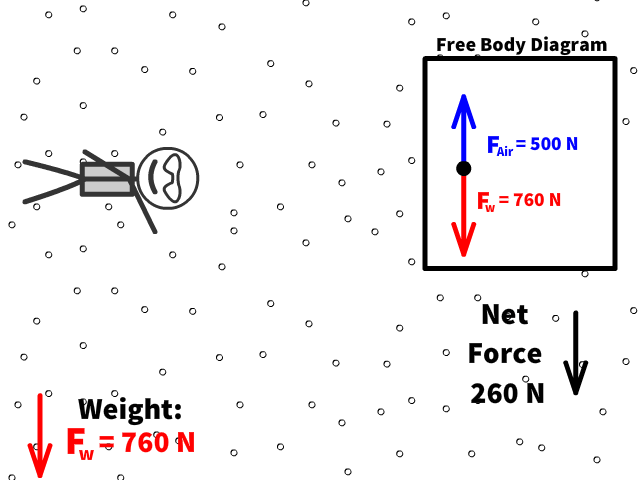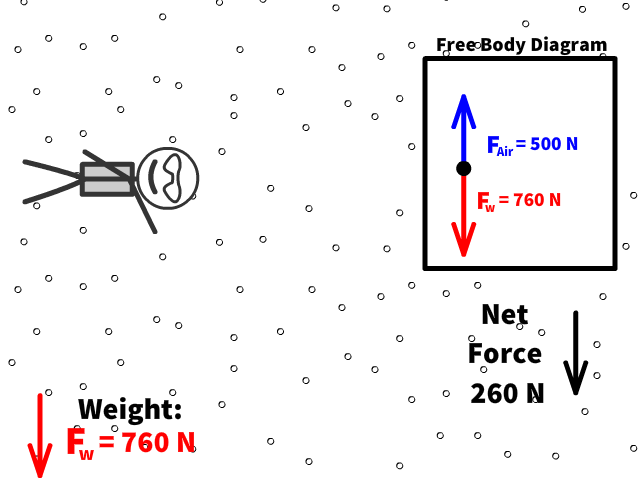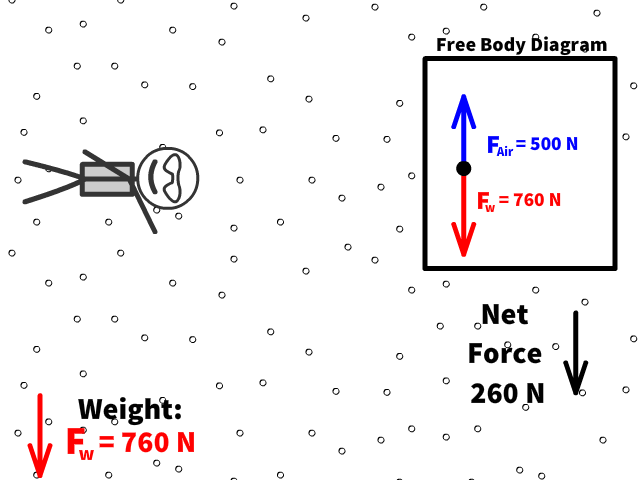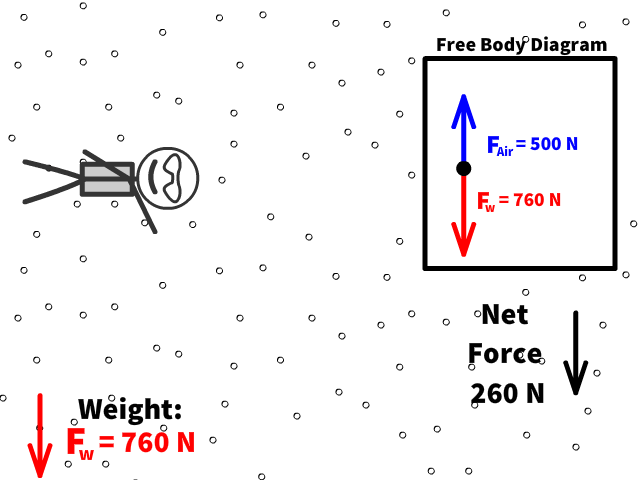
Q8: What is Caleb’s new acceleration now with air resistance of 500 N?
Q9: What is Caleb’s new net force when air resistance is 760 N?
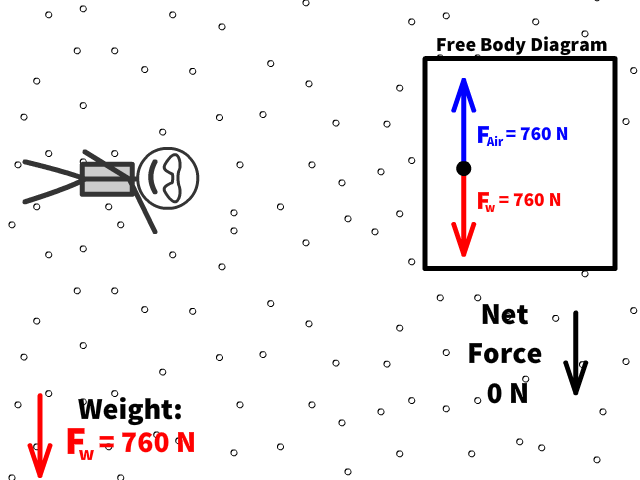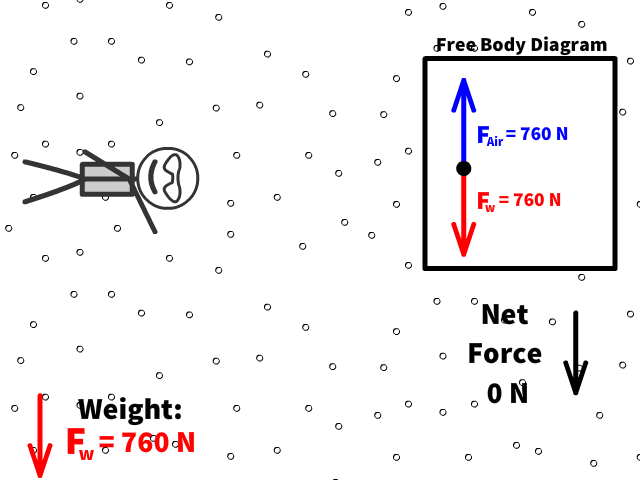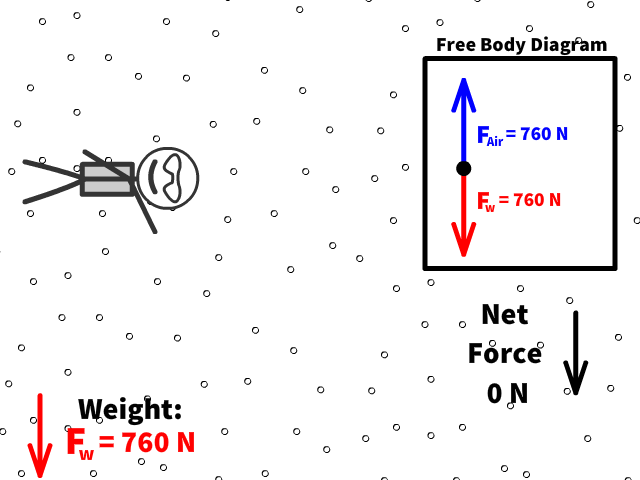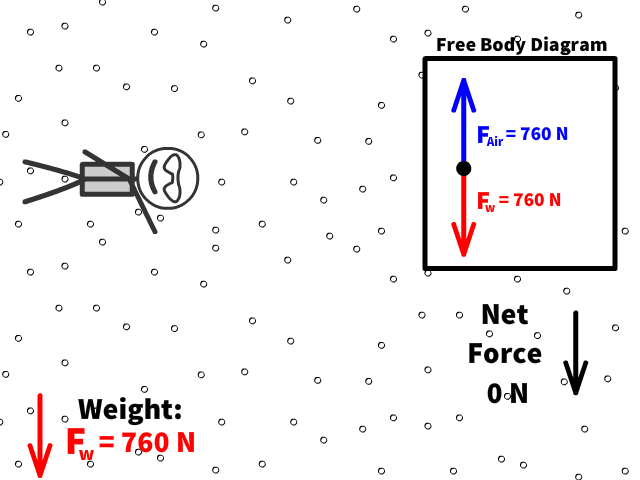
Q10: What is Caleb’s new acceleration now that there is 760 N of air resistance?
As an object falls:
- It’s weight pulls down causing acceleration
- Air resistance increases in the opposite direction
- The result is that net force and acceleration decrease
- The object increases its speed but by less
- Until terminal velocity
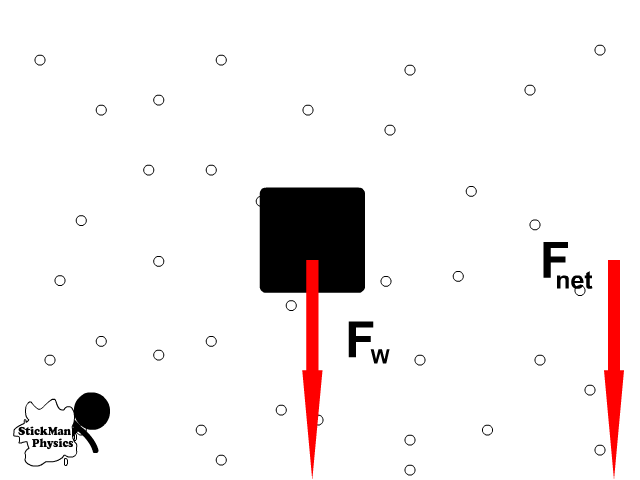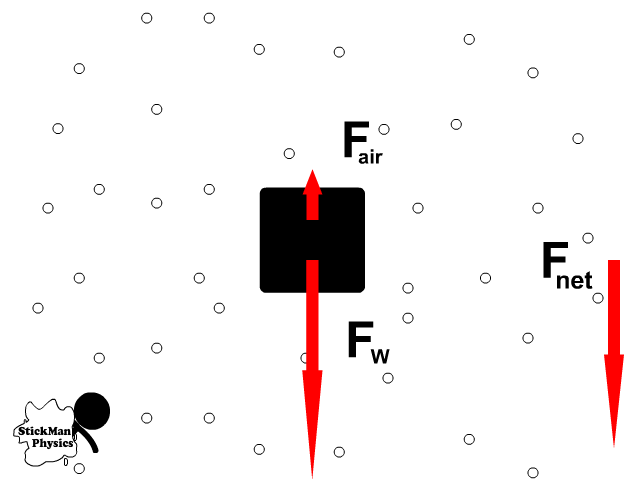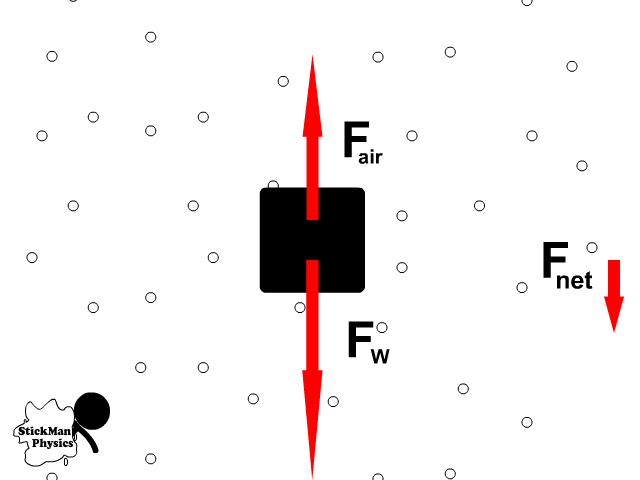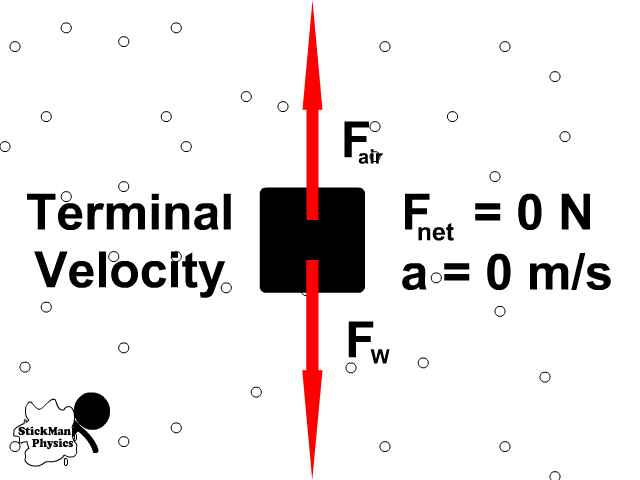
Terminal Velocity:
Terminal velocity is the point when a persons weight equals the air resistance force
At terminal velocity:
- There is no net force
- Fair= -Fw
- Therefore no acceleration
- A person falls with constant velocity
- Terminal velocity depends on the shape of an object
- Terminal velocity is around 53 m/s or 122 mph for a human skydiver
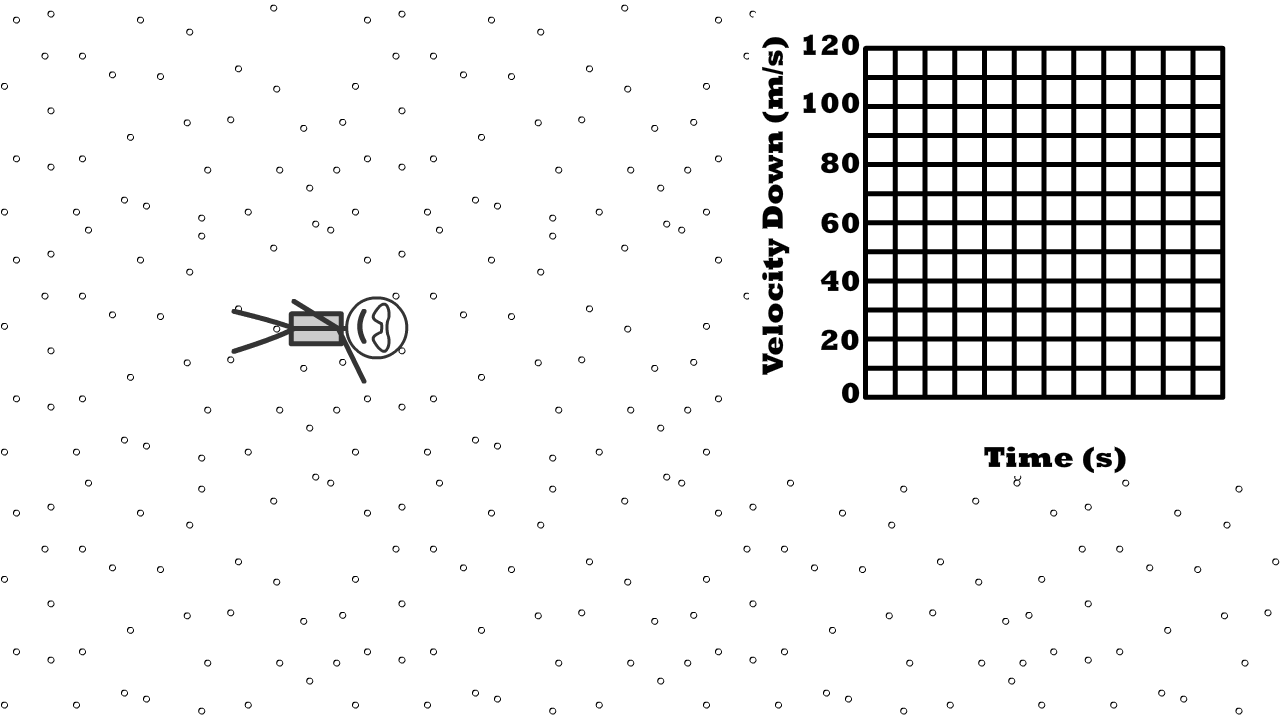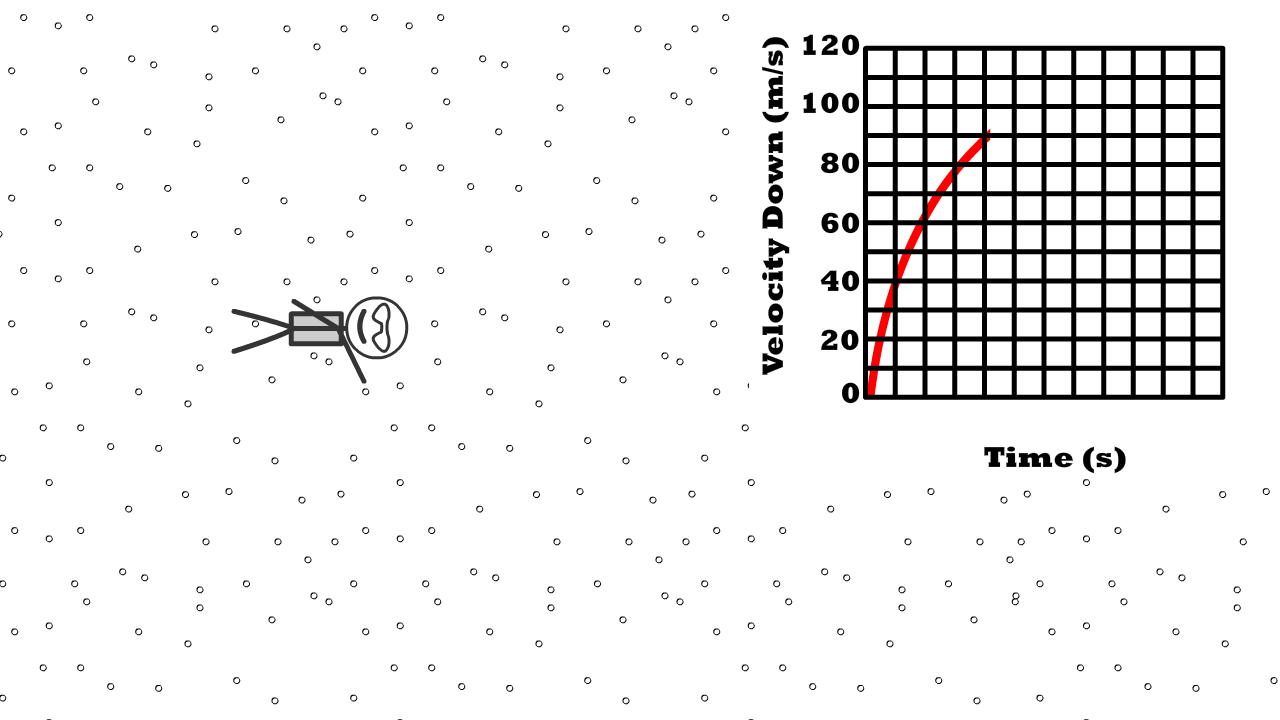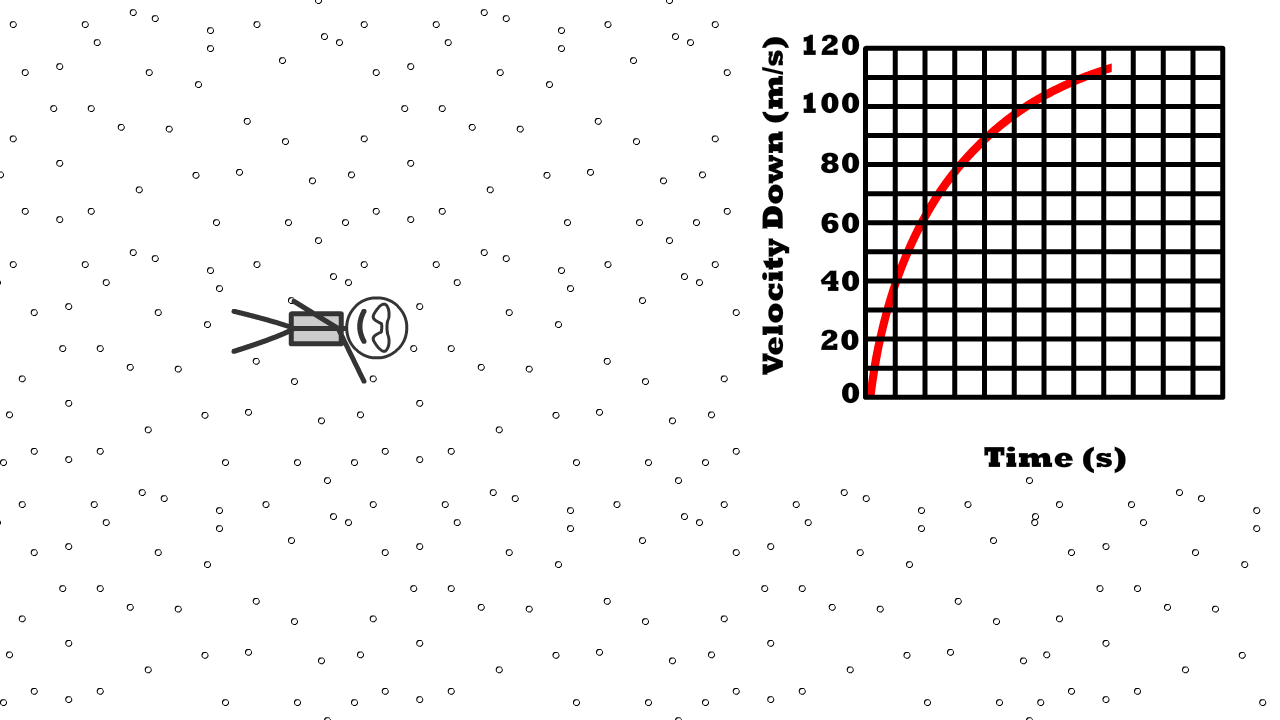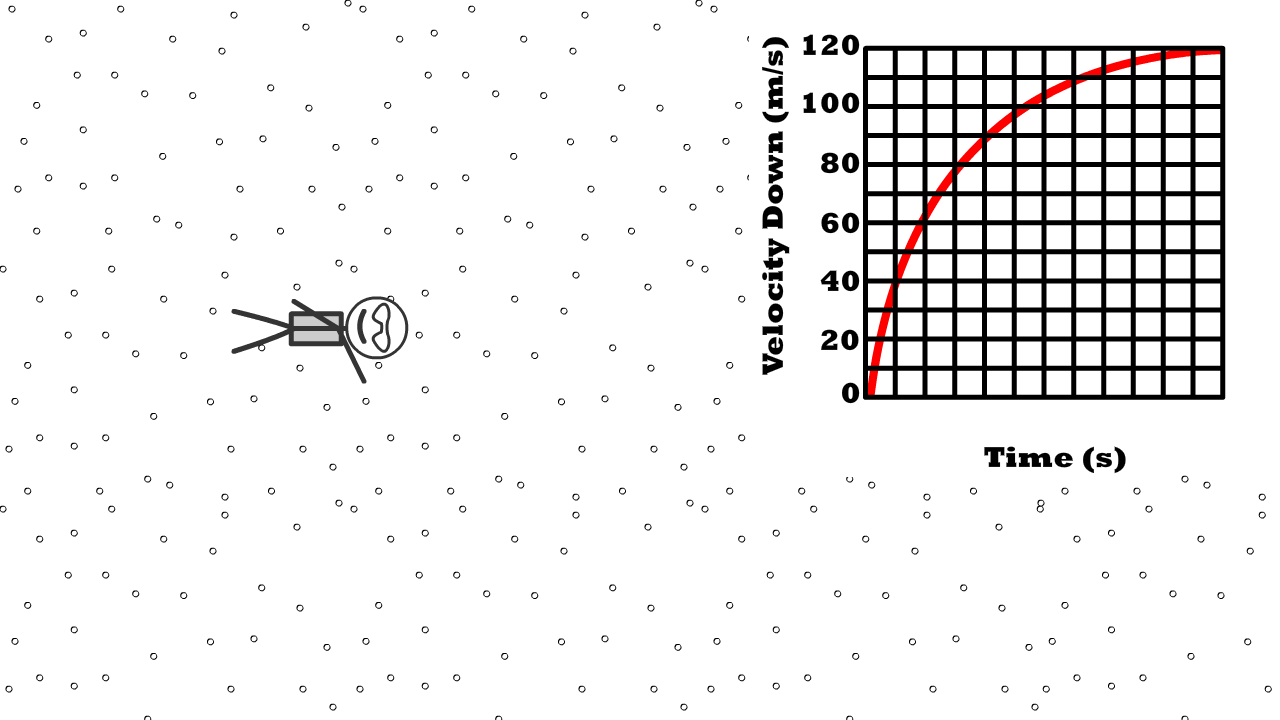
Q11: What shape does a velocity time graph have at terminal velocity?
Q12: Describe air resistance compared to weight, net force, and acceleration at terminal velocity
Q13: What is 76 kg Caleb’s weight at terminal velocity?
Q14: What is the air resistance on 76 kg Caleb at terminal velocity?
Q15: What is the net force on Caleb at terminal velocity?
Q16: What is the acceleration of Caleb at terminal velocity?
Q17: What is 76 kg Caleb’s new net force when air resistance increases to 1000 N after pulling out the parachute?
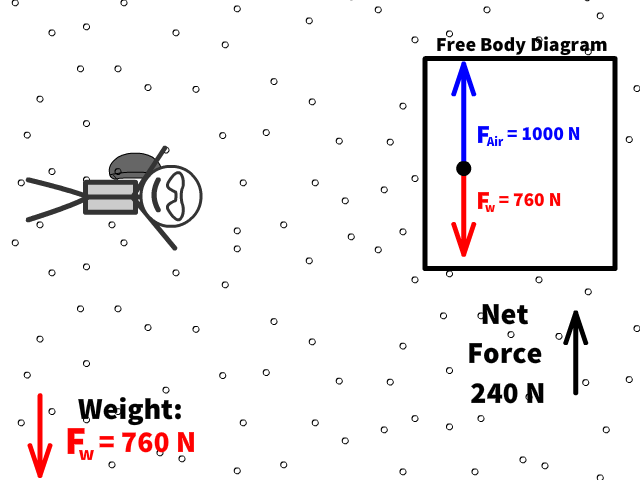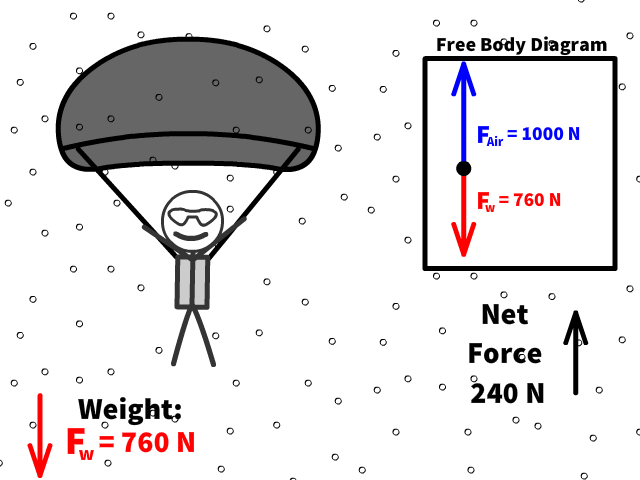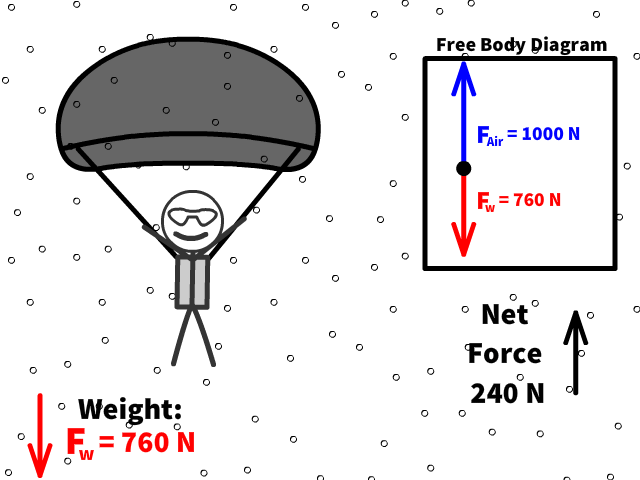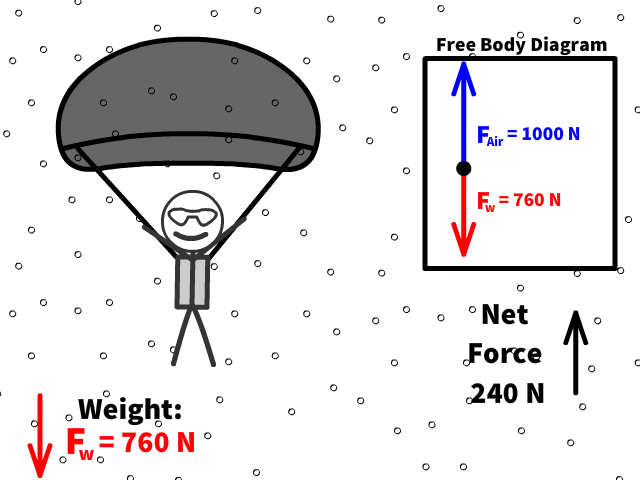
Q18: What is Caleb’s new acceleration now that there is a net force of 240 N up?
Q19: Is Caleb going up when the acceleration is up when the parachute opens?
Q20: Is Caleb accelerating or decelerating when the parachute opens?
Air Resistance Questions:
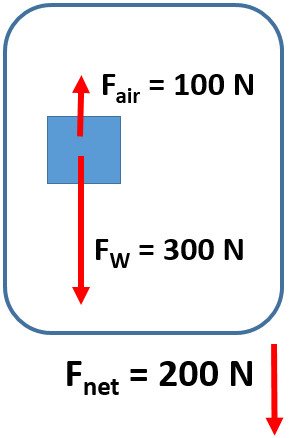
1. Draw a force diagram of an object with a weight of 300 N when 100 N of air resistance is encountered?
2. What is the acceleration of an object with a weight of 300 N when 100 N of air resistance is encountered?
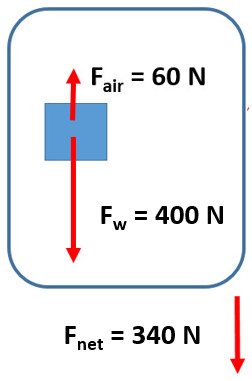
3. Draw a force diagram of a 40 kg object that encounters 60 N of air resistance?
4. What is the acceleration of a 40 kg object that encounters 60 N of air resistance?
Links
- Continue to Friction
- Back to the Main Forces Page
- Back to the Stickman Physics Home Page
- Equation Sheet